Marielle
Remillard - REU 2007
Marielle
Remillard
studies mathematics and biology at Austin College.
She came to CSU in 2007 for the Summer Water
REU program. During that time, she prepared a report for the
New Mexico Bureau of Reclamation on the geomorphic and hydraulic
characteristics of the Galisteo Reach of the Rio Grande. She
is passionate about water resources and one day hopes to promote
the sustainable use of water resources as a global water
analyst..
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
 Kevin
Hanegan - REU 2008 Kevin
Hanegan - REU 2008
Kevin
is completing his senior year at Louisiana State University
majoring in Civil Engineering. He came to CSU the summer of 2008
as part of the NSF's REU program in water resources. Along with
Quentin Benally, Kevin worked to update the USBR reach report for
the San Felipe reach of the Middle Rio Grande. He performed
hydraulic and geomorphic analysis for the study reach using
HEC-RAS, Arc-GIS, and other analysis techniques. After graduation,
Kevin plans to pursure a masters in either coastal engineering or
general hydraulics. te students at CSU have been examining the Middle
Rio Grande for several years. Changes to the river, induced
by the installation of several dams and channelization, have led
the US Bureau of Reclamation in Albuquerque, NM to commission
hydraulic summary reports of several reaches in the river,
including the 10-mile long Rio Puerco and 6.15-mile long San
Felipe Reaches. Both reaches are also included in the habitat
designation for two federally listed endangered species, the Rio
Grande silvery minnow and the southwestern willow flycatcher. In
order to facilitate restoration efforts for these species, it has
been necessary to determine the historic, current and potential
future geomorphic configuration of the channel. Kevin is
currently a PhD student at the University of New Orleans working
in coastal engineering.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________
 Quentin
Benally - AGEP-McNAIR 2008 Quentin
Benally - AGEP-McNAIR 2008
Quentin
is attending the Engineering program at San Juan College in
Farmington, New Mexico. He joined Dr. Julien’s team in the
summer of 2008 as a research participant in CSU’s Alliancefor
Graduate
Education and the Professoriate (Agep-McNair), which was aimed
toward students with an interest in pursuing a Masters Degree or
PhD. He worked with Kevin Hanegan, under the supervision of
Dr. Julien and Seema Shah-Fairbank, with the Hydraulic Analysis of
the San Felipe Reach, Middle Rio Grande, from Arroyo Tonque to
Angostura Diversion Dam. He gained research experience,
working with databases, hydraulic analysis using HEC-RAS, historic
planform observations
using Arc-GIS, and other traditional research techniques. In
the report, he also shared his knowledge of the area and affects
of past management to the surrounding Indian communities.
After finishing at SJC, he plans to earn a Civil Engineering
degree from a nearby university. After experiencing
research, working at the Engineering Research Center, meeting new
people, enjoying the local environment, Fort Collins and CSU is a
possibility.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________

Duangrudee
Kositgittiwong - Visiting Scientist in 2008 - PhD
dissertation
Duangrudee
Kositgittiwong
received a Ph.D. from King Mongkut’s University of
Technology Thonburi (KMUTT), Bangkok, Thailand. She previously
graduated from KMUTT in 2005 with a B.Eng. in Civil Engineering.
She studied maximum scour downstream of bed sills for her senior
project. After that, she works for Water Resources Engineering
Research Laboratory, WAREE lab., as a research assistant. She
got the Royal Golden Jubilee Ph.D. program scholarship to study
in master and Ph.D. program, in water resources engineering, in
Thailand. She came to CSU, as an exchange visitor, since January
2009 to study and do her research for a year. She is interested
in flow through stepped spillways. Gambit and Fluent model were
used in the research to work for flow computation.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________

Anna
Paris - Visiting Scientist in 2008-09
Sediment
analysis of the Gila
River
Anna
Paris joined Dr. Julien’s team in November 2008 as a Visiting
Scientist. She graduated from University
of Trento
(Italy)
in October 2008 with a MS in Environmental Engineering focused
on hydraulics. She has been studying debris flows mechanics both
experimentally and numerically at the CUDAM hydraulics lab in Trento
developing for her Master’s thesis a resistance formula able to
describe debris flow behavior ranging from mature debris flow to
hyperconcentrated bed load transport. She got a scholarship from
FTU in Italy
to continue her studies concerning River Engineering and
Hyperconcentrated flows at CSU. In Fort Collins, she
developed a statistical-numerical sediment analysis of Gila
River (Arizona)
and has been working on the hydraulic analysis of the Middle Rio
Grande for the USBR. The object of study was a 20-miles
long reach stretching from the Arroyo de las Cañas
to the South Boundary Bosque del Apache in central New Mexico. The change in hydraulics and
morphology over the last 50 years has been studied using
software as ArcGIS and HEC-RAS. An interesting phenomenon was
also observed: during 2008 the downstream part of the Bosque
reach had been experiencing a strong aggradation due to the
creation of a sediment plug.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________

Katharine
Anderson - REU 2009 and RA2011
Katharine
studies both civil engineering with a concentration in soil
and water resources and music at Colorado State University.
She participated in the Summer Water REU Program in 2009 to
analyze the Bosque Reach in the Middle Rio Grande. This
analysis was completed utilizing ArcGIS, HEC-RAS and Excel.
She helped prepare a report for the Bureau of Reclamation on the
geomorphic and hydraulic characteristics of the 23-mile-long
reach. In 2011, she helped analyze a second reach, the
Elephant Butte Reach, for the Bureau of Reclamation. This
32-mile-long reach is a continuation from the southern end of the
Bosque Reach and ends at Elephant Butte Dam. Due to human
influence on the river, the Middle Rio Grande has changed
excessively over the past century and many species of native
plants and animals have become endangered. Katharine
is interested in river hydraulics and water resources, and hopes
to someday pursue a Master’s degree.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________

Michelle
Ida Anslem - Undergraduate Scholar 2011
Michelle
Ida Anslem is an invited undergraduate scholar from UiTM Shah
Alam, Malaysia
for integrated research program at Engineering Research Center of
Colorado State University. She is in her final year now for her
studies in Bachelor of Civil Engineering. She worked with Dr.
Julien during Fall 2011 on the preparation of Arc-GIS input files
for the hydrologic model TREX. She
contributed to the modeling analysis of the Naesung Stream in Korea
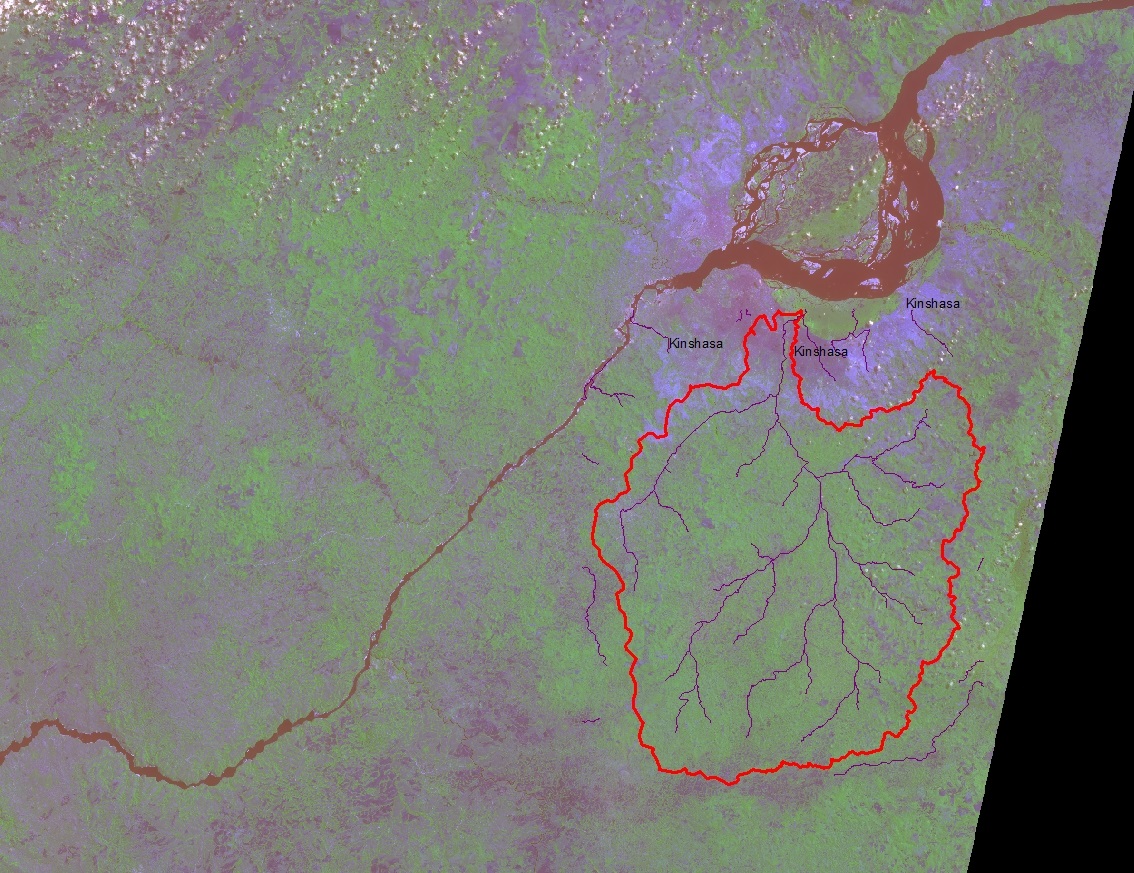
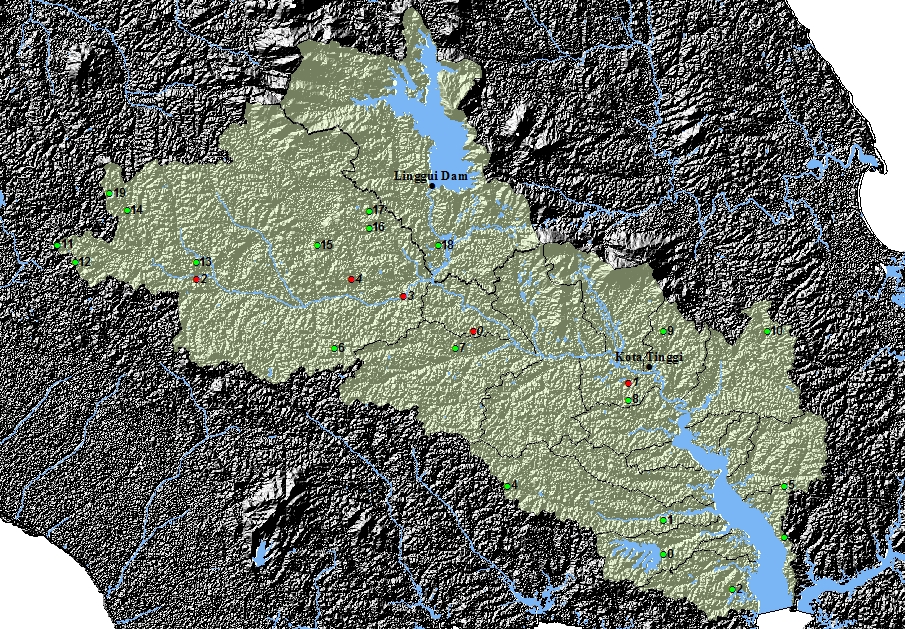
and the Kota Tinggi River of Malaysia. Michelle
was
also involved in processing multiple GIS cross section and the
particle size distributions on the Rio Grande
in New Mexico. She learned about data management and
report preparation for various hydraulic structures.
She also hopes to pursue her Master’s Degree in
hydraulics or hydrology in the near future.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________

Ladislav
Rousar - Visiting Scientist 2013-14
Ladislav
Rousar
graduated in Civil Engineering from Brno University of
Technology (Czech Republic), Institute of Water Structures, in
2011. He continues in Ph.D. program with interest in
hydraulics. He has been studying numerical models
for the upper channel of the Prelouc II lock (unsteady
1D model, HEC-RAS) and conducted a parametric study on dike
roughness (steady 2D, SMS). He came to CSU, as an exchange
visitor, on fall semester 2013 for better understanding the
mechanisms of sedimentation and erosion. His doctoral thesis
will deal with the determination of incipient motion of
homogenous and non-homogenous gravel-bed at high relative
roughness and full turbulent flow. Experiments on incipient of
motion are verified with field measurements. In
additional, his research incorporates a comparison of
velocities profiles measured by UVP and those calculated by
numerical models (3D, ANSYS-CFX). With laser scanned bed, he
can experimentally determine fall velocity of natural particles
and measure bed-load transport over a rectangular
broad-crested weir.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________

Dr.
Jai Hong Lee - Visiting Scientist 2013- Professor at South
Carolina State University
Dr. Jai Hong Lee is a
postdoctoral research associate with a strong interest in
hydrologic research related to climate change. 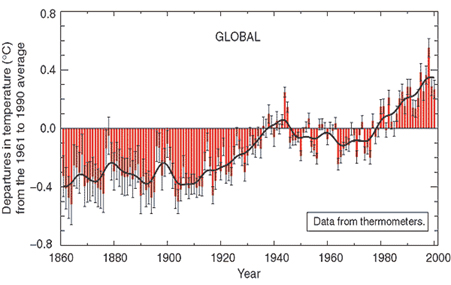 He majored in hydrology and
earned a Ph.D. degree at
Hanyang University as well as a professional engineer
certificate. He worked as a member of design and research
team at the Korea Rural Development Corporation, RDC, as a
researcher and lecturer for the Department of Civil
Engineering at Hanyang University, and as an executive
director of the water resources department at the B&Y
engineering institute. He carried out a hydrologic
analysis of Si-Hwa Sea Barrier Project in 2002, and a
hydraulic analysis of the Han River Project in 2005 for
the Ministry of Construction and Transportation. He majored in hydrology and
earned a Ph.D. degree at
Hanyang University as well as a professional engineer
certificate. He worked as a member of design and research
team at the Korea Rural Development Corporation, RDC, as a
researcher and lecturer for the Department of Civil
Engineering at Hanyang University, and as an executive
director of the water resources department at the B&Y
engineering institute. He carried out a hydrologic
analysis of Si-Hwa Sea Barrier Project in 2002, and a
hydraulic analysis of the Han River Project in 2005 for
the Ministry of Construction and Transportation.
His
primary research interest is in the rainfall-runoff
analysis of extreme flood such as PMF(Probable Maximum
Flood). He is in search for understanding the hydrologic
and meteorological impact of climate change, temporal and
spatial distribution of rainfall, rainfall-runoff analysis
for dam design and river improvement, and reservoir
routing and operation. His final goal is to develop an
optimal process to accurately estimate extreme storms and
floods for the improved design of hydraulic and flood
regulation structures. Consequently, accurate estimates
of extreme storms and floods would be most important to
develop a plan for flood damage mitigation and prevention
as well as a disaster management policy.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________

Christoph
Matzke - Visiting Scientist 2014-15 
Christoph visited CSU from July
to December 2014 under a Marshall Plan Scholarship to
study hydraulic losses in aerated surge tank throttles. He
graduated in Civil Engineering from KIT Karlsruhe in 2008.
He worked on different international engineering projects
(Geotechnics, Hydropower, Tunneling, Construction and
Consulting) for 3 years before returning to the university
to write his doctoral thesis at the Unit of Hydraulic
Research of the University of Innsbruck in Austria.
His doctoral thesis will deal with the determination
of the hydraulic losses of an aerated surge tank throttle.
To investigate the impact of the aeration on the hydraulic
losses, a physical model was constructed in the hydraulic
lab in Innsbruck. Lots of data were collected of these
experiments. While visiting CSU, Christoph mainly worked
on his experimental data analysis. He also enjoyed the
Erosion and Sedimentation class of Prof. Pierre Y. Julien,
which was a great opportunity to learn more about
related aspects of hydraulic engineering. Thanks!
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________

Dr.
Jose Anderson Batista - Visiting Scientist 2015-16
Landslides happen every year all
around the world with different spatial densities. As much
as the landslide density increase, more the mud and
debris flow advances through downstream canals causing
severe damages to the overbank infrastructure and
occupation. Such damages often
reach more than one billion US dollars. In Brazil, the
more vulnerable region to landslides is comprehended by
the Atlantic Highland Landform
(ranged from 13 to 26 lat. degrees), where some of the
richest cities are located. Between 2011 and 2014 severe
storms triggered landslides
with more than 10 slides per squared kilometer, causing
thousands of deaths and destroying thousands of buildings
in about ten cities.
The aim of this research is to
find the natural causes and to model the overall process
until the overbank deposit of the 2014's landslides in
Itaoca,
where the landslide scars can be more clearly identified
by satellite imagery.
The results reached herein are the basis for up coming
researches aimed to predict and early warn overbank
deposits.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________

George
Marino Soares Gonçalves - Undergraduate Scholar 2015
George
Marino Soares Gonçalves is a
Water Engineering student in Brazil at UFPEL and
he’s been focusing his major in hydraulics and
hydrology.
As
an undergraduate
scholar from
Florida Institute
of Technology, he
joined a summer
research project
at the ERC
(Engineering
Research Center)
of Colorado State
University in
summer 2015.
George Marino participated in a governmental
program called BSMP (Brazilian Mobility Science
Program) which gave him the opportunity
to meet Professor Pierre Y. Julien and come to
CSU. George spent the entire 2015 summer at CSU
working with Dr. José Anderson do Nascimento
Batista
on a GRASS GIS 7.0 based manual which focused in
watershed morphology functions.
The result of this project can be found online as
“User’s guide to GIS GRASS 7.0 for Watershed
Morphology” or clicking on the link below.
George Marino wishes go back to Brazil and finish
his Water Engineering major and pursue a Master
degree in hydraulics in the future.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________

Dr.
Seongjoon Byeon - Visiting Scientist 2016 - 17
Dr.
SeongJoon Byeon is a postdoctoral
visiting scholar. He received his
BSc degree in Civil Engineering,
his M.S. degree and Ph.D. degree
in Hydroinformatics from Incheon
National University, Korea, in
2005, 2008 and 2015 respectively.
He has also received his M.S.
degree and Ph.D. degree in
EuroAQUAE Hydroinformatics from
University of Nice Sophia
Antipolis, France in 2007 and
2014. His research interest
includes the combination of
computer science and water
engineering. He has solid
laboratory research experience, as
he has been working as a
researcher, performing design and
analysis work for a number of big
water projects. Aside from
computer laboratory work, he has
field work experience including
experiments of the hydraulic
characteristics of river
structures. He visited DHI in
Denmark in 2005, and again as an
intern in 2007, where he learned
about the use of various DHI
softwares and successfully
performed research. His current
research mainly focuses on the
smart water grid. Many problems
that are encountered in regards to
water balance and resources
management are related to
challenges of economic development
under limited resources and tough
competition among various water
uses. In order to overcome these
difficulties, water management has
to articulate and combine several
resources in order to respond to
various demands while preserving
the ecological quality of the
environment.
In addition, he also carried out
several researches on experiments
to investigate hydraulic
characteristics of river
structures.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________.

Dr.
Lingyun Li - Visiting Scientist 2016 - 17
Dr. Lingyun Li came to CSU as a
visiting scholar in 2016. He received his bachelor degree
and doctoral degree in Department of Hydraulic Engineering
in Tsinghua University, China, in 2005 and 2010
respectively. His doctoral thesis dealt with the
relationship between the alluvial river morphology and the
flow and sediment regime. He worked as a researcher at the
Changjiang River Scientific Research Institute, China,
since 2010. His research interest includes the river
mechanics and sediment transport. His current research
mainly focuses on the delayed response of geomorphology of
river channel on the altered flow and sediment regime.
While visiting CSU, Dr. Li mainly worked on analysis the
different characteristic of the flow discharge, sediment
load, and river channel in the middle and lower reach of
Yangtze River in China pre- and post the Three Gorges dam
operation. He also carried out a presentation about the
delayed response model of Yangtze River during his stay.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________.

Dr.
Joonhak Lee - Visiting Professor 2017
Catena article on soil erosivity
Joon-hak
Lee joined Dr. Julien’s team in
July 2016 as a visiting scholar.
He completed his Ph.D. in Civil
and Environmental Engineering at
Yonsei University in South Korea.
One of his committee members was
Prof. Jose Salas at Colorado State
University, and his chief advisor
at Yonsei University was Prof.
Jun-haeng Heo who obtained his
Ph.D. from Colorado State
University. He has been a tenured
associate professor in Civil and
Environmental Engineering at Korea
Military Academy since 2014.
Dr. Lee’s research interests are
rainfall erosivity, soil erosion
and sedimentation, statistical
hydrology & hydraulics,
landslides and GIS modeling. He is
a principal investigator of
“Development of Rainfall Erosivity
Model in Korea (2015 – 2018)”
supported by the National Research
Foundation of Korea (NRF). His
main research in USA is focused on
investigating the relationship
between rainfall erosivity and
sedimentation.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________.

Dr.
Eunkyung Jang - Visiting Scientist 2017 - 18
Catena article on specific
degradation data mining
Dr.
Eun-kyung Jang have been a
researcher at CSU Julien's lab
since September 2017. She
graduated with a BS (2010), MS
degrees (2012), and completed her
Ph.D. (2017) from Civil and
Environment Engineering at Myongji
University in Korea. Dr. Jang
researched the sediment discharge
assessment to develop the optimum
method using Data Mining for Ph.D.
Dissertation.
Until recently, she worked at
Korea Institute of Civil
Engineering and Building
Technology (KICT) where the
organization researches
construction policies and develops
technologies in Korea. Currently,
she is focusing on studies related
to hydraulic engineering and river
mechanics. Sediment analysis for
Nakdong River at the confluence
and stable channel design for
Cheongmi, Wonju, Naesung Stream
are the main projects. She has
also published and expected to
publish the journal papers (KSCE,
IJSR etc.).
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________.

Dr.
Xudong Chen - Visiting Professor 2017 - 18
Dr.
Xudong Chen has been a researcher
at CSU Julien's lab since December
2017. She got her B.S. (2009) and
Ph.D. (2014) degree, in Hydraulic
Structure Engineering, from Hohai
University in China. Dr. Chen
studied the dam safety evaluation
to develop the analysis methods
for working behavior evolution of
Roller Compacted Concrete (RCC)
dams for Ph.D. Dissertation.
Until recently, she worked as an
assistant professor at the water
conservancy and environment
department of Zhengzhou University
in China. Research area of the
department lies in water
resources, hydrologic and
hydraulic engineering. Currently,
she is focusing on studies related
to hydraulic engineering and river
mechanics. Seepage safety
evaluation for RCC Longtan dam
under the influences of water
pressure, temperature and time
effect is the main objective. She
is expected to publish some
conference and journal papers on
dam safety during her stay.
______________________________________________________________________________________________________

Dr.
Alisher N. Khazratov – Visiting Scholar 2021 khazratov@gmail.com
Alisher
came to CSU from August to
December 2021 as a visiting
scholar from Uzbekistan under
Faculty Enrichment Program. His
research interest includes
numerical modeling of sediment
transport (1D, HEC-RAS 1D and 2D),
stable canal design, and river
morphology. During his stay in
CSU, he carried out LSPIV
experiments with Professor Robert
Ettema to investigate bendway
weirs and rock vanes. He
also participated in the Erosion
and Sedimentation class of
Professor Pierre Y. Julien to
deepen his knowledge in sediment
transport processes.
|

 Sangdo An is
graduate student in Civil Engineering at Colorado State
University.
Sangdo An is
graduate student in Civil Engineering at Colorado State
University. 












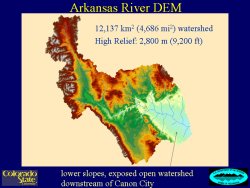 Estimates of extreme floods and probabilities are
needed for hydrologic engineering and dam safety risk
analysis. Physically-based, distributed watershed models are
used
as
an avenue to estimate extreme floods, and as a basis to
extrapolate frequency curves. This research focuses on applied
hydrology and hydraulics of extreme floods on large watersheds. The main elements of this
Estimates of extreme floods and probabilities are
needed for hydrologic engineering and dam safety risk
analysis. Physically-based, distributed watershed models are
used
as
an avenue to estimate extreme floods, and as a basis to
extrapolate frequency curves. This research focuses on applied
hydrology and hydraulics of extreme floods on large watersheds. The main elements of this 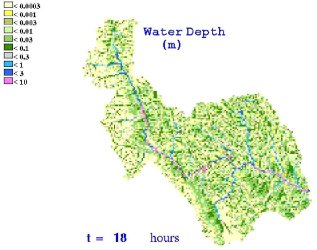 research include improving and using a
two-dimensional, physically-based rainfall-runoff model (CASC2D)
to estimate extr
eme
floods and probabilities for dam safety on a large (12,000 km2)
watershed, the Arkansas River above Pueblo, Colorado. New
tools have been
developed, including a channel mesh generator, so the model can be
applied at this scale. The main research goals are to:
demonstrate that CASC2D can be used to simulate extreme floods on
large watersheds; and add new process components, including
extreme storms and initial conditions, so that CASC2D can be used
to develop a flood frequency curve. In addition, we are
conducting sensitivity studies to examine: the spatial
distribution of storm rainfall with area and elevation; storm
duration; initial soil saturation; and channel floodplains; and
their effects on the model flood frequency curve extrapolation,
hydrograph shape, timing, peak and volume.
research include improving and using a
two-dimensional, physically-based rainfall-runoff model (CASC2D)
to estimate extr
eme
floods and probabilities for dam safety on a large (12,000 km2)
watershed, the Arkansas River above Pueblo, Colorado. New
tools have been
developed, including a channel mesh generator, so the model can be
applied at this scale. The main research goals are to:
demonstrate that CASC2D can be used to simulate extreme floods on
large watersheds; and add new process components, including
extreme storms and initial conditions, so that CASC2D can be used
to develop a flood frequency curve. In addition, we are
conducting sensitivity studies to examine: the spatial
distribution of storm rainfall with area and elevation; storm
duration; initial soil saturation; and channel floodplains; and
their effects on the model flood frequency curve extrapolation,
hydrograph shape, timing, peak and volume.

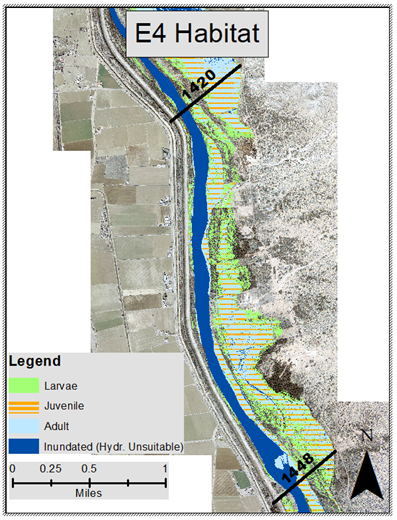
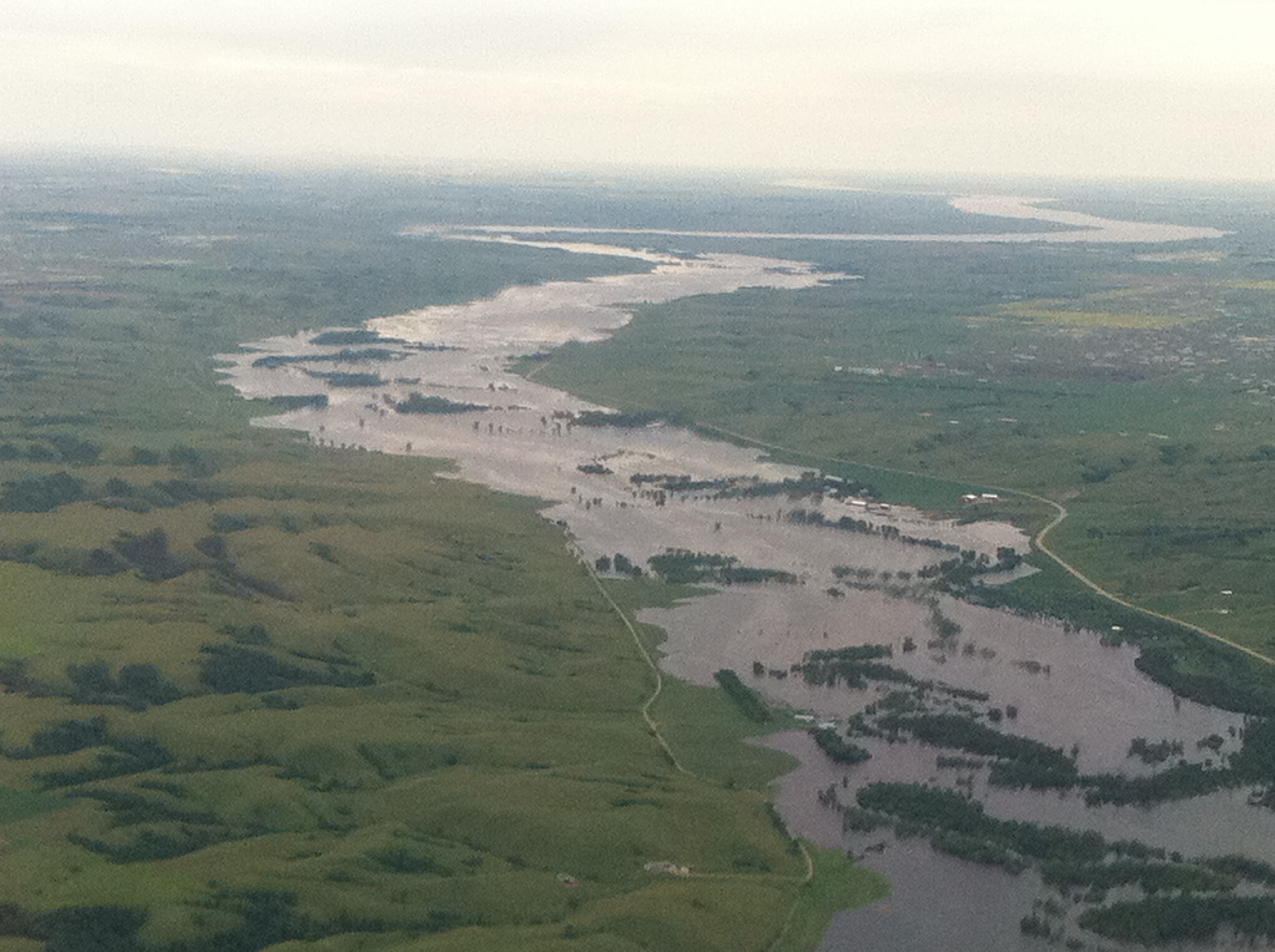
 Caitlin is a Master’s student
studying hydraulic engineering at Colorado State University. She
obtained her Bachelor’s degree in Ecological Engineering from
Oregon State University in 2019. She is most interested in a
career in stream restoration or river engineering. Caitlin’s
research has been focused on determining where critical habitat is
along the Rio Grande for an endangered species of fish known as
the Silvery Minnow. Currently, her work has focused on assisting
with the creation of a process linkage report between Isleta and
San Acacia reaches. This report will draw connections between
geomorphology, morphodynamics, hydrology, and biology that can be
used to define suitable habitat for the Silvery Minnow.
Caitlin is a Master’s student
studying hydraulic engineering at Colorado State University. She
obtained her Bachelor’s degree in Ecological Engineering from
Oregon State University in 2019. She is most interested in a
career in stream restoration or river engineering. Caitlin’s
research has been focused on determining where critical habitat is
along the Rio Grande for an endangered species of fish known as
the Silvery Minnow. Currently, her work has focused on assisting
with the creation of a process linkage report between Isleta and
San Acacia reaches. This report will draw connections between
geomorphology, morphodynamics, hydrology, and biology that can be
used to define suitable habitat for the Silvery Minnow. 
 Noah
Friesen is a Masters student in the hydraulics and river
mechanics program at CSU. After getting a BS in Civil
Engineering in 2005 from CSU, he returned for graduate school in
the spring of 2006. He spent the summer of 2006 in Las Vegas,
Nevada working at the Desert Research Institute, which is the
research branch of the University of Nevada system.
Noah
Friesen is a Masters student in the hydraulics and river
mechanics program at CSU. After getting a BS in Civil
Engineering in 2005 from CSU, he returned for graduate school in
the spring of 2006. He spent the summer of 2006 in Las Vegas,
Nevada working at the Desert Research Institute, which is the
research branch of the University of Nevada system.
 Weather Service River Forecast System's Sacramento Soil Moisture
Accounting (SAC-SMA) program to create a conceptual soil moisture
routine for the TREX model. By accounting for the soil moisture
recovery and return flows, the new model will bridge the gap
between major runoff events and allow for mid- to long-term
hydrophysical
modeling.
Weather Service River Forecast System's Sacramento Soil Moisture
Accounting (SAC-SMA) program to create a conceptual soil moisture
routine for the TREX model. By accounting for the soil moisture
recovery and return flows, the new model will bridge the gap
between major runoff events and allow for mid- to long-term
hydrophysical
modeling.

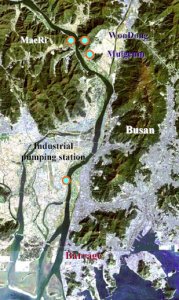 n Ji was a PhD student of the hydraulic
engineering program in Civil Engineering at Colorado State
University (CSU) and she came from Korea. She graduated from
Myoungji University in Korea with a BS and MS degrees in Civil and
Environment Engineering. In Korea, she worked for several research
projects, during the graduate course, such as the experimental and
numerical studies and field works related to hydraulics, hydrology
and water management. Also, she has been studying the sediment
transport, river mechanics, river rehabilitation, fluvial
geomorphology etc in the hydraulic engineering program at CSU.
n Ji was a PhD student of the hydraulic
engineering program in Civil Engineering at Colorado State
University (CSU) and she came from Korea. She graduated from
Myoungji University in Korea with a BS and MS degrees in Civil and
Environment Engineering. In Korea, she worked for several research
projects, during the graduate course, such as the experimental and
numerical studies and field works related to hydraulics, hydrology
and water management. Also, she has been studying the sediment
transport, river mechanics, river rehabilitation, fluvial
geomorphology etc in the hydraulic engineering program at CSU.  intrusion in the estuary and prevent a
large flood due to high tides. The channel of Nakdong River was
designed to convey a design flood of 18,300 cubic meters per
second. The estuary barrage impacts the Lower Nakdong River in the
following fields: hydraulics, hydrology, sedimentation,
water-quality and stream ecology. Especially, because of the
construction of the barrage, the Lower Nakdong River has
experienced sedimentation problems requiring dredging operation
annually. The primary purpose of the dredging operations is to
maintain the conveyance capacity of the channel in the event of a
large flood combined with high water levels during high tides. The
recent historical record shows dredging volumes of about 400,000
cubic meters of dredged material per year. The material dredged is
primarily non-cohesive very fine sand.
intrusion in the estuary and prevent a
large flood due to high tides. The channel of Nakdong River was
designed to convey a design flood of 18,300 cubic meters per
second. The estuary barrage impacts the Lower Nakdong River in the
following fields: hydraulics, hydrology, sedimentation,
water-quality and stream ecology. Especially, because of the
construction of the barrage, the Lower Nakdong River has
experienced sedimentation problems requiring dredging operation
annually. The primary purpose of the dredging operations is to
maintain the conveyance capacity of the channel in the event of a
large flood combined with high water levels during high tides. The
recent historical record shows dredging volumes of about 400,000
cubic meters of dredged material per year. The material dredged is
primarily non-cohesive very fine sand.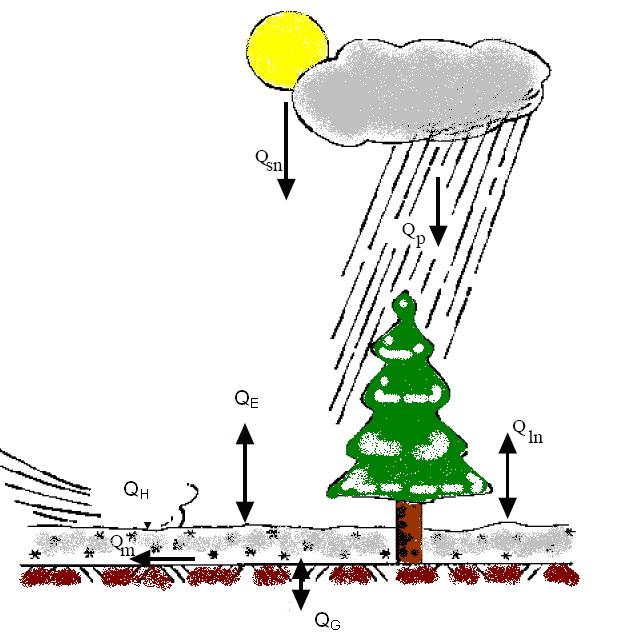
 CASC2D
framework has been developed since 1991 by Dr. Julien and his students. CASC2D is
the numerical integrated surface
hydrology and sedimentation program. Additionally, it can provide
the runoff and sediment transport movies with time series.
CASC2D
framework has been developed since 1991 by Dr. Julien and his students. CASC2D is
the numerical integrated surface
hydrology and sedimentation program. Additionally, it can provide
the runoff and sediment transport movies with time series. 








 in
May
of 2006.
After
years of living on the plains, her favorite part about living in
Colorado is seeing the mountains every day.
in
May
of 2006.
After
years of living on the plains, her favorite part about living in
Colorado is seeing the mountains every day. 


 atrick
Ndolo Goy received his bachelor degree in Civil Engineering
with distinction from the University of Kinshasa,
atrick
Ndolo Goy received his bachelor degree in Civil Engineering
with distinction from the University of Kinshasa, 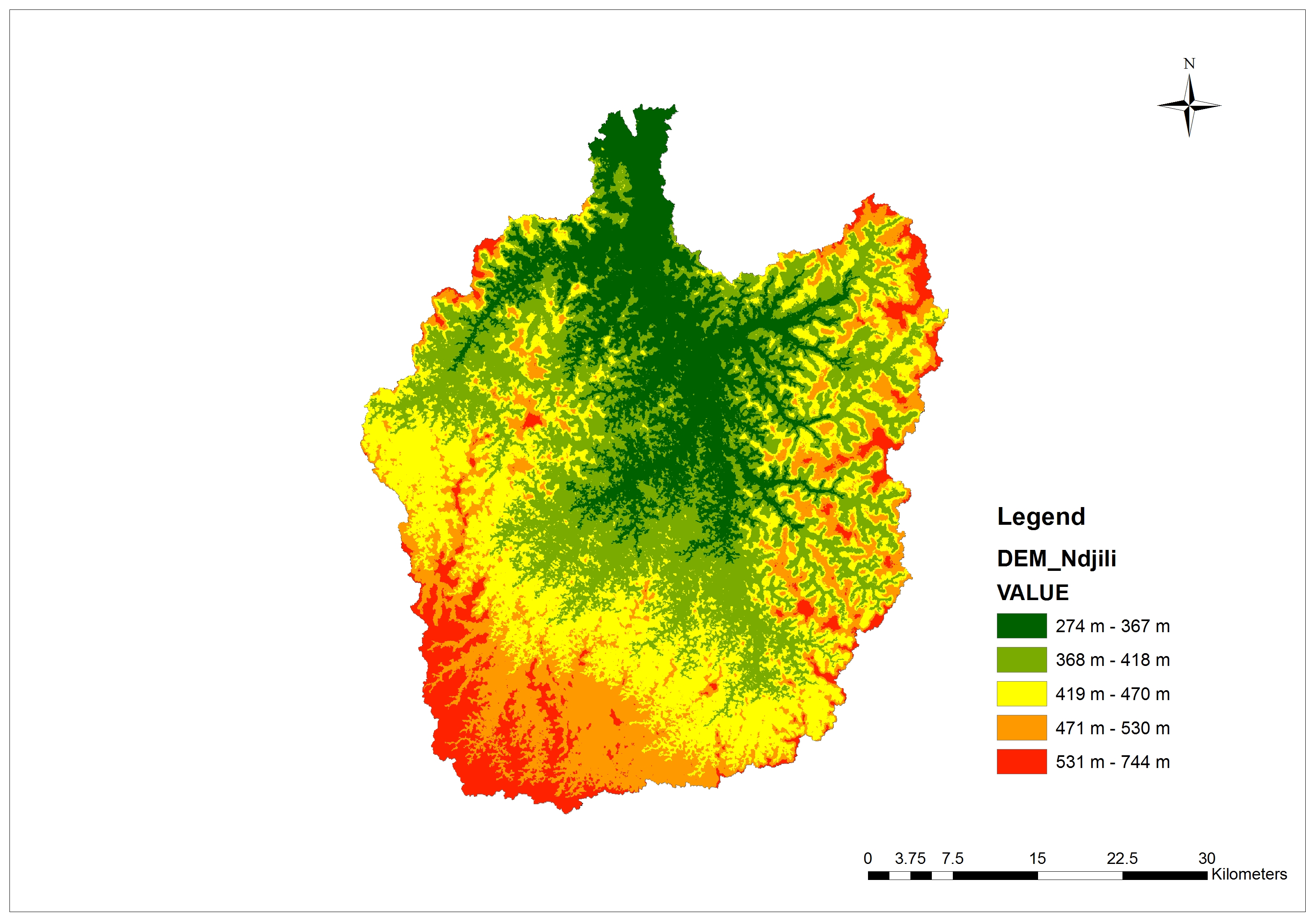 DR
Congo, in 2006. After he graduated, he was appointed deputy
chief of staff of the Materials and Soil Mechanics laboratory
of the University of Kinshasa for which he conducted more than
one hundred major geotechnical studies in DR Congo, Rep. of
Congo, and Burundi. From 2009 to 2012, he helped teach 3
classes as Teaching Assistant (Soil mechanics, hydrology and
hydraulic classes). As member of the Nile Basin Initiative
Network for DR Congo, Patrick was involved in the
implementation of the Decision Support System of the Nile
Basin between 2008 and 2011. He was awarded a Fulbright
Scholarship from State Department in 2013 to complete a
Master’s degree in Hydraulics and River Mechanics at Colorado
State University. After completing his Master’s degree,
Patrick is planning in enrolling in PhD program in Hydraulic
engineering.
DR
Congo, in 2006. After he graduated, he was appointed deputy
chief of staff of the Materials and Soil Mechanics laboratory
of the University of Kinshasa for which he conducted more than
one hundred major geotechnical studies in DR Congo, Rep. of
Congo, and Burundi. From 2009 to 2012, he helped teach 3
classes as Teaching Assistant (Soil mechanics, hydrology and
hydraulic classes). As member of the Nile Basin Initiative
Network for DR Congo, Patrick was involved in the
implementation of the Decision Support System of the Nile
Basin between 2008 and 2011. He was awarded a Fulbright
Scholarship from State Department in 2013 to complete a
Master’s degree in Hydraulics and River Mechanics at Colorado
State University. After completing his Master’s degree,
Patrick is planning in enrolling in PhD program in Hydraulic
engineering.
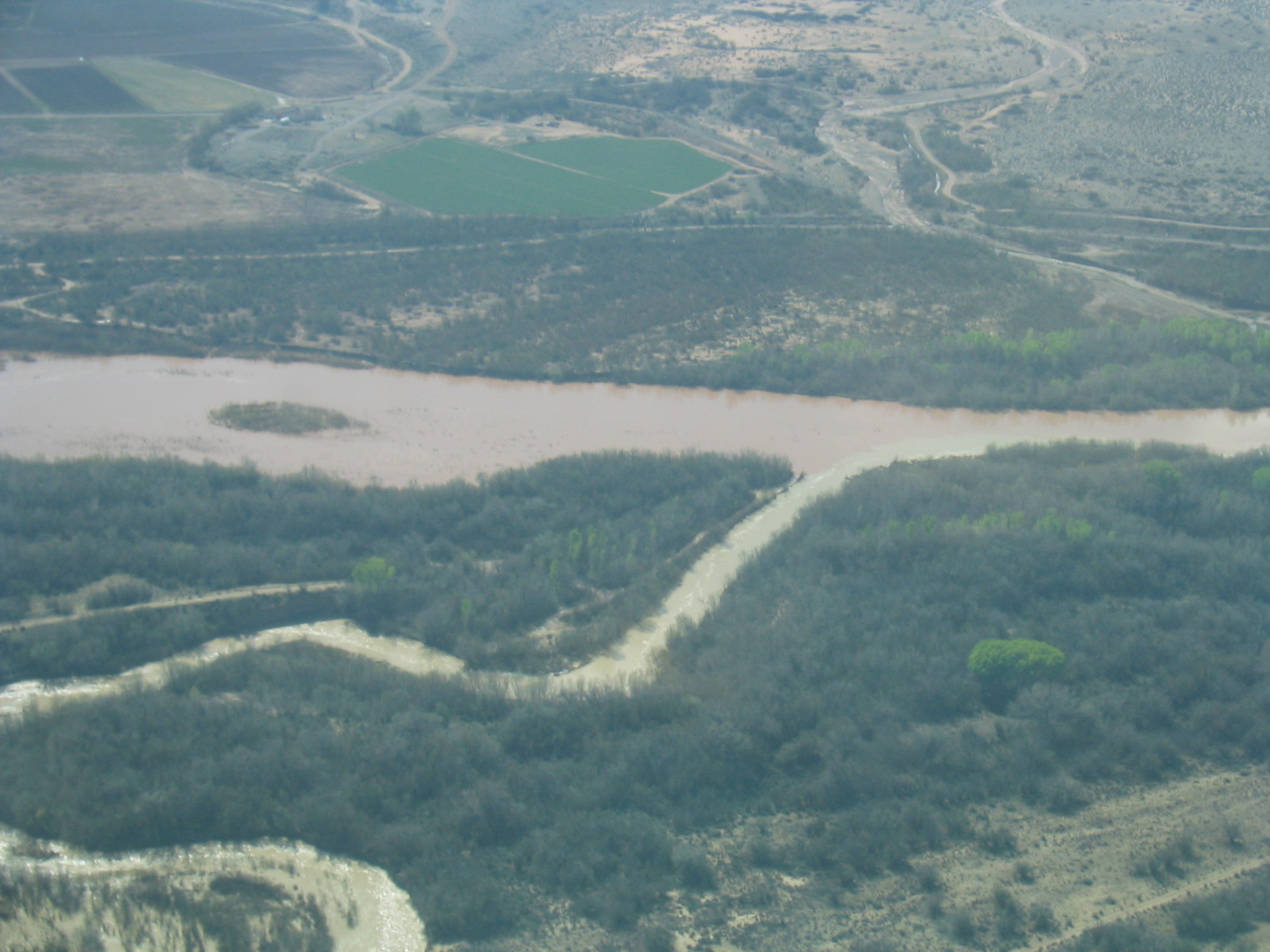
 The purpose
of this project was to update this database with the most recent
possible data, using sources such as the U.S. Bureau of
Reclamation office, U. S. Geological Survey, and the USBR reports.
The data, analyses for each reach studied in the Middle Rio
Grande, and the reports themselves were organized into an
interactive database DVD that can be accessed like a webpage.
Through this, it is possible to view analyses from each reach of
the Rio Grande, each report, and the theses and dissertations
written by the students who have worked on this project for the
past several years.
The purpose
of this project was to update this database with the most recent
possible data, using sources such as the U.S. Bureau of
Reclamation office, U. S. Geological Survey, and the USBR reports.
The data, analyses for each reach studied in the Middle Rio
Grande, and the reports themselves were organized into an
interactive database DVD that can be accessed like a webpage.
Through this, it is possible to view analyses from each reach of
the Rio Grande, each report, and the theses and dissertations
written by the students who have worked on this project for the
past several years.

![C:\Documents and Settings\b0etepso\Local Settings\Temporary Internet Files\Content.Word\MSH_09_20_2007_207[1].jpg](O%27brien.jpg)



 Tracy is a Masters student at
Colorado State University, majoring in Hydraulic Engineering.
Tracy is a Masters student at
Colorado State University, majoring in Hydraulic Engineering.




 Kiyoung
Park is a graduate student of hydraulics in Civil
Engineering at Colorado State University. He is currently
studying
Kiyoung
Park is a graduate student of hydraulics in Civil
Engineering at Colorado State University. He is currently
studying



 in Helena, Montana. While obtaining his bachelor’s degree he worked for
the Federal Highway Administration for almost two years.
in Helena, Montana. While obtaining his bachelor’s degree he worked for
the Federal Highway Administration for almost two years.


 He
received his undergrad degree from Colorado School of Mines in
Civil Engineering in 2018 and worked in consulting for stream
restoration and water resources engineering before beginning grad
school in 2020. Whenever he can, Andrew is outside backpacking in
Colorado/Wyoming, trying out new recipes, or wandering around Fort
Collins.
He
received his undergrad degree from Colorado School of Mines in
Civil Engineering in 2018 and worked in consulting for stream
restoration and water resources engineering before beginning grad
school in 2020. Whenever he can, Andrew is outside backpacking in
Colorado/Wyoming, trying out new recipes, or wandering around Fort
Collins.

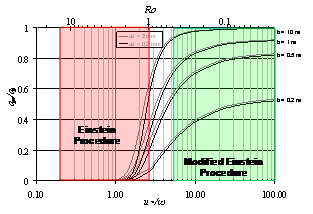 Seema
Shah-Fairbank completed her graduate studies in Civil
Engineering at Colorado State University.
Seema
Shah-Fairbank completed her graduate studies in Civil
Engineering at Colorado State University.
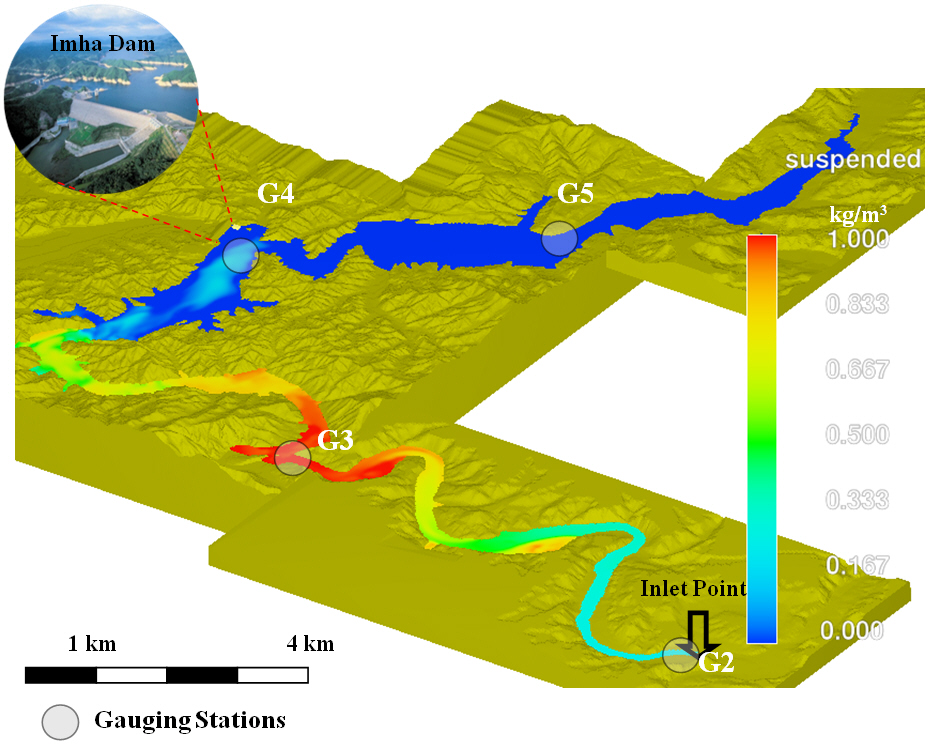
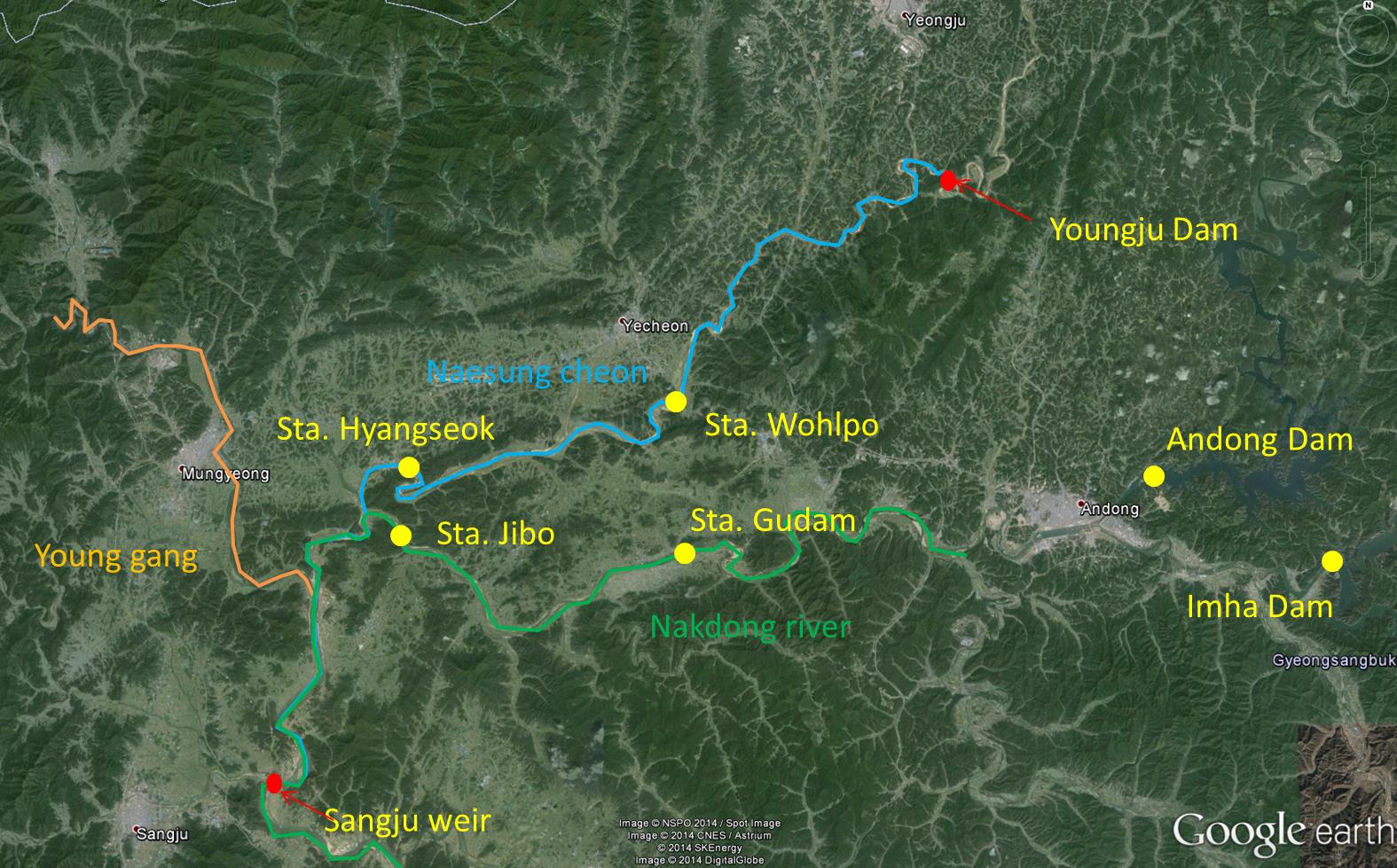
 Young-ho Shin will take the analysis effects on downstream river channel using aerial photographs which
taken before and after dam construction. The study focuses on the
aspect of water, sediment and vegetation interaction in the sand bed channel
where the river flow is regulated by upstream dams, in order
words, hydro-geomorphologic changes in a sand bed channel and thus
vegetation expansion on the sandbars in the channel by changes in
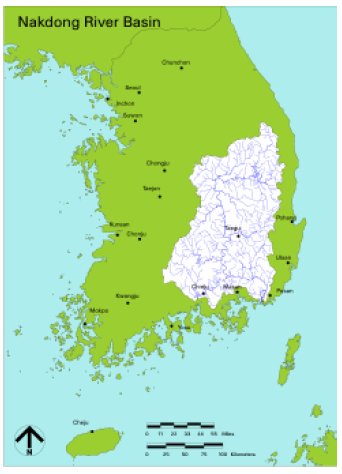
the flow regime. The study area is the Nakdong River in Korea.
This river
is the longest river in South Korea with its river length of
506km. The basin area of the river is 23,394km2, the second
largest after the Han River (32,200km2). It locates in the south
east of the Korean Peninsula and generally the river flows from
north to south. The riverbed is composed mostly of sands except in
the far upstream in the mountain area where it is composed of gravel and cobble. In the river basin,
dams have been built since 1970’s starting from the Andong Dam in
1976. Since then, more major dams including the Imha Dam (completed in 1991)
and Hapcheon Dam (completed in 1988) have been built for flood
control, water supply and hydroelectric power generation. Also,
estuary barrage which is located at the end of Nakdong River have
been built to reduce salt-water intrusion and prevent a large
flood due to high tides.
Young-ho Shin will take the analysis effects on downstream river channel using aerial photographs which
taken before and after dam construction. The study focuses on the
aspect of water, sediment and vegetation interaction in the sand bed channel
where the river flow is regulated by upstream dams, in order
words, hydro-geomorphologic changes in a sand bed channel and thus
vegetation expansion on the sandbars in the channel by changes in
the flow regime. The study area is the Nakdong River in Korea.
This river
is the longest river in South Korea with its river length of
506km. The basin area of the river is 23,394km2, the second
largest after the Han River (32,200km2). It locates in the south
east of the Korean Peninsula and generally the river flows from
north to south. The riverbed is composed mostly of sands except in
the far upstream in the mountain area where it is composed of gravel and cobble. In the river basin,
dams have been built since 1970’s starting from the Andong Dam in
1976. Since then, more major dams including the Imha Dam (completed in 1991)
and Hapcheon Dam (completed in 1988) have been built for flood
control, water supply and hydroelectric power generation. Also,
estuary barrage which is located at the end of Nakdong River have
been built to reduce salt-water intrusion and prevent a large
flood due to high tides.  He
also received his Bachelor's of Science from Colorado State
University in Civil Engineering. In his free time, Joshua rock
climbs, skiis, hikes, and travels.
He
also received his Bachelor's of Science from Colorado State
University in Civil Engineering. In his free time, Joshua rock
climbs, skiis, hikes, and travels.
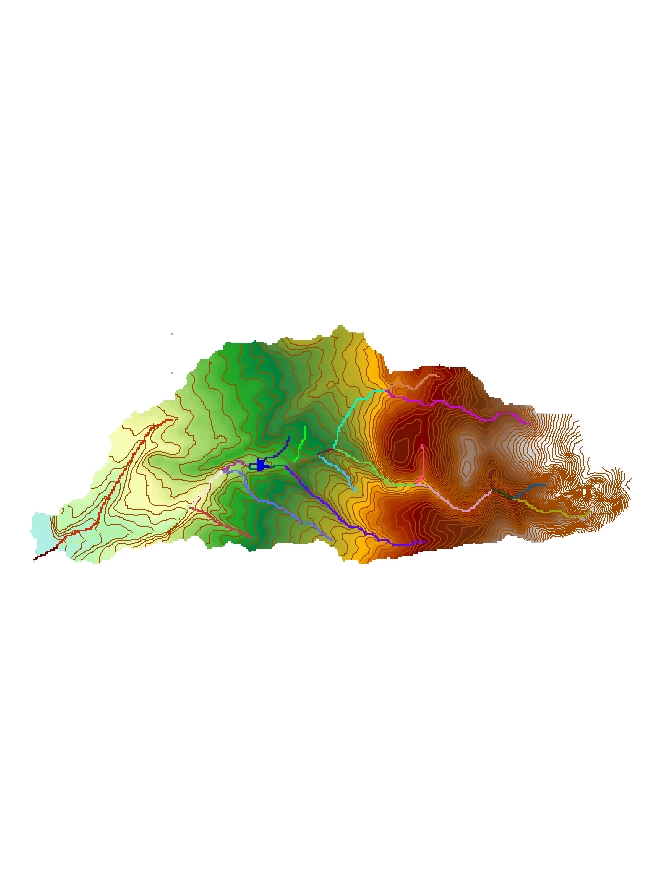
 Andy Steininger is a master’s
degree candidate studying hydraulics and hydrology in the Civil
and Environmental Engineering Department at Colorado State
University.
Andy Steininger is a master’s
degree candidate studying hydraulics and hydrology in the Civil
and Environmental Engineering Department at Colorado State
University.
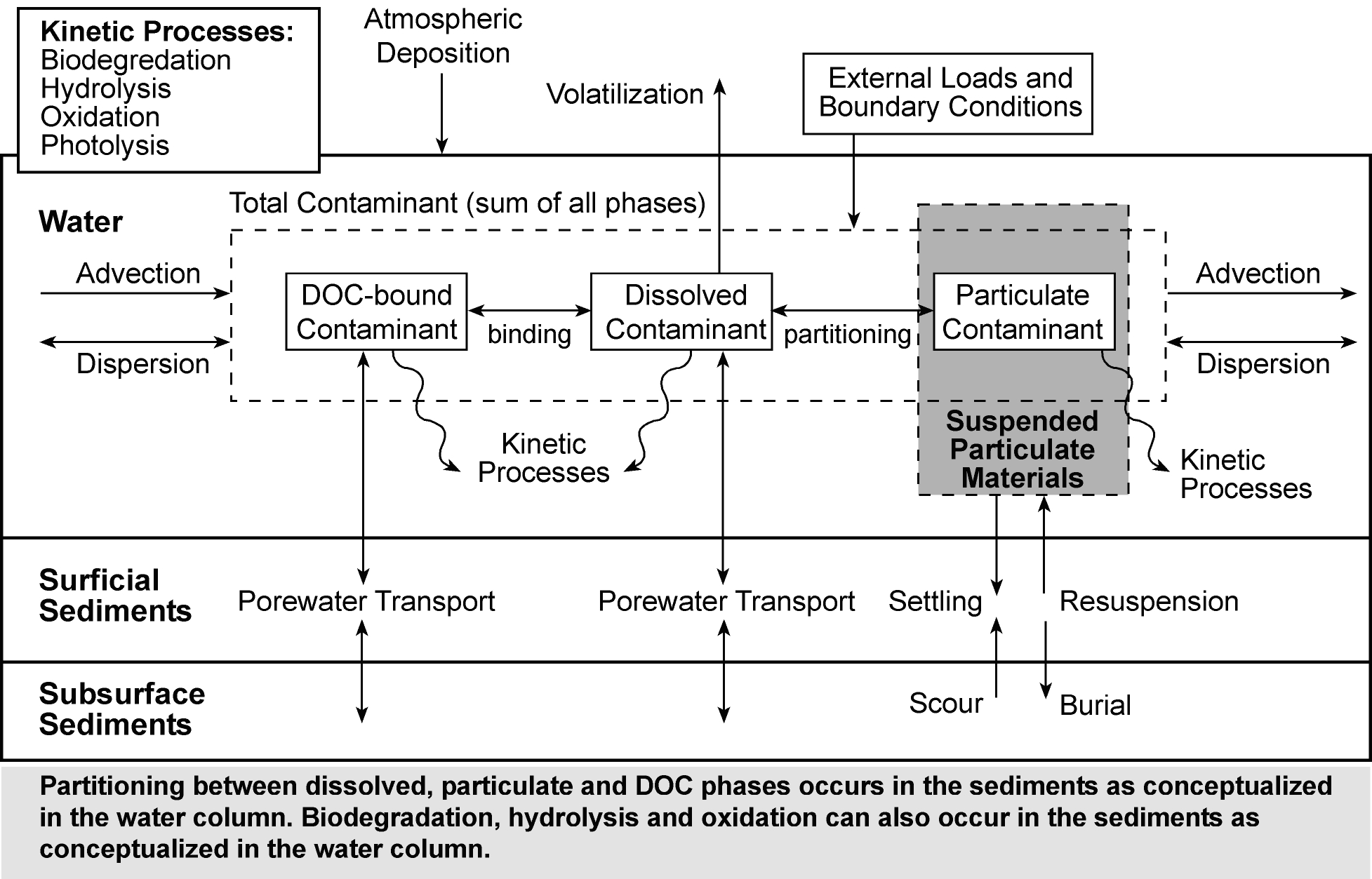
 To meet this need, a numerical model to
simulate the transport and fate of chemicals across watersheds is
under development. The model development effort focuses on surface
water hydrology with an emphasis on the transport and fate of
particle-associated chemicals. A computer code that integrates the
most critical hydrologic, sediment transport, and chemical
transport and fate processes into a single framework was developed
(Figure 1). This new code is called the Two-dimensional Runoff,
Erosion, and eXport (TREX) model and is based on Colorado State
University’s CASC2D watershed model with chemical transport and
fate processes from the USEPA WASP and IPX series of stream water
quality models.
To meet this need, a numerical model to
simulate the transport and fate of chemicals across watersheds is
under development. The model development effort focuses on surface
water hydrology with an emphasis on the transport and fate of
particle-associated chemicals. A computer code that integrates the
most critical hydrologic, sediment transport, and chemical
transport and fate processes into a single framework was developed
(Figure 1). This new code is called the Two-dimensional Runoff,
Erosion, and eXport (TREX) model and is based on Colorado State
University’s CASC2D watershed model with chemical transport and
fate processes from the USEPA WASP and IPX series of stream water
quality models.

 I
am a part-time graduate student in hydraulic engineering at
Colorado State University. Both Oregon State University and CSU
felt obliged to offer me a bachelors and masters degree in civil
engineering, respectively. In between school and work I managed to
become a licensed professional engineer in Oregon and a registered
professional hydrologist through the American Institute of
Hydrology. In order to insure that my graduate studies progress at
a glacial pace, I currently work as the forest hydrologist on the
White River National Forest in Glenwood Springs.
I
am a part-time graduate student in hydraulic engineering at
Colorado State University. Both Oregon State University and CSU
felt obliged to offer me a bachelors and masters degree in civil
engineering, respectively. In between school and work I managed to
become a licensed professional engineer in Oregon and a registered
professional hydrologist through the American Institute of
Hydrology. In order to insure that my graduate studies progress at
a glacial pace, I currently work as the forest hydrologist on the
White River National Forest in Glenwood Springs.



















