What is Chemical and Biological Engineering?¶
Science can amuse and fascinate us all, but it is engineering that changes the world.
—Isaac Asimov
Chemical and Biological Engineering
Chemical and Biological Engineers apply their knowledge of chemistry, biology, and engineering principles to design and optimize processes and systems that involve chemical reactions, biochemical transformations, and the manipulation of biological systems. They work on developing new materials, designing and optimizing chemical reactors, developing sustainable energy sources, creating pharmaceutical drugs and vaccines, and improving the production of food and beverages.
Opportunities and challenges in CBE¶
Sustainable Energy Production: Developing efficient and sustainable methods for energy production, including renewable energy sources and advanced fuel technologies, to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change.
Carbon Capture and Utilization: Developing technologies to capture and store carbon dioxide emissions from industrial processes and power plants, as well as finding innovative ways to convert captured carbon into valuable products.
Water Resource Management: Addressing the scarcity of clean water resources by developing efficient and sustainable methods for water treatment, desalination, and wastewater management to ensure a reliable supply of clean water.
Advanced Materials: Designing and developing new materials with enhanced properties and functionalities for various applications, such as lightweight and high-strength materials, advanced catalysts, biomaterials, and drug delivery systems.
Bioprocess Engineering: Advancing the field of bioprocess engineering to enable large-scale production of biofuels, biopharmaceuticals, and other bio-based products, while optimizing process efficiency and reducing costs.
Personalized Medicine and Healthcare: Integrating engineering principles with biology and medicine to develop personalized diagnostics, therapeutics, and medical devices that improve patient outcomes, including targeted drug delivery systems and regenerative medicine approaches.
Systems Biology and Synthetic Biology: Advancing our understanding of complex biological systems through computational modeling and data-driven approaches, as well as engineering new biological systems for applications in healthcare, agriculture, and environmental sustainability.
Process Intensification and Manufacturing Efficiency: Developing innovative techniques for process intensification to maximize efficiency and reduce the environmental impact of chemical and biological manufacturing processes, including miniaturization, continuous processing, and the use of advanced automation and control systems.
Sustainable Food Production: Developing sustainable and efficient methods for food production, including precision agriculture, alternative protein sources, waste reduction, and optimizing the use of resources in food processing and preservation.
Global Health and Disease Prevention: Applying chemical and biological engineering principles to address global health challenges, such as developing affordable and accessible vaccines, diagnostics, and treatments for infectious diseases, as well as improving sanitation and access to clean water in developing regions.
THIS IS AN EXCITING TIME TO BE A CHEMICAL AND BIOLOGICAL ENGINEER!
Exercise: Areas of interest in CBE
Based on the information presented, in what areas of Chemical and Biological Engineering do you have an interest?
Introduce yourself to the students sitting next to you and discuss with them three areas of CBE that seem interesting to you.
CBE course sequence at CSU¶
At a high level, these are the core CBE courses:
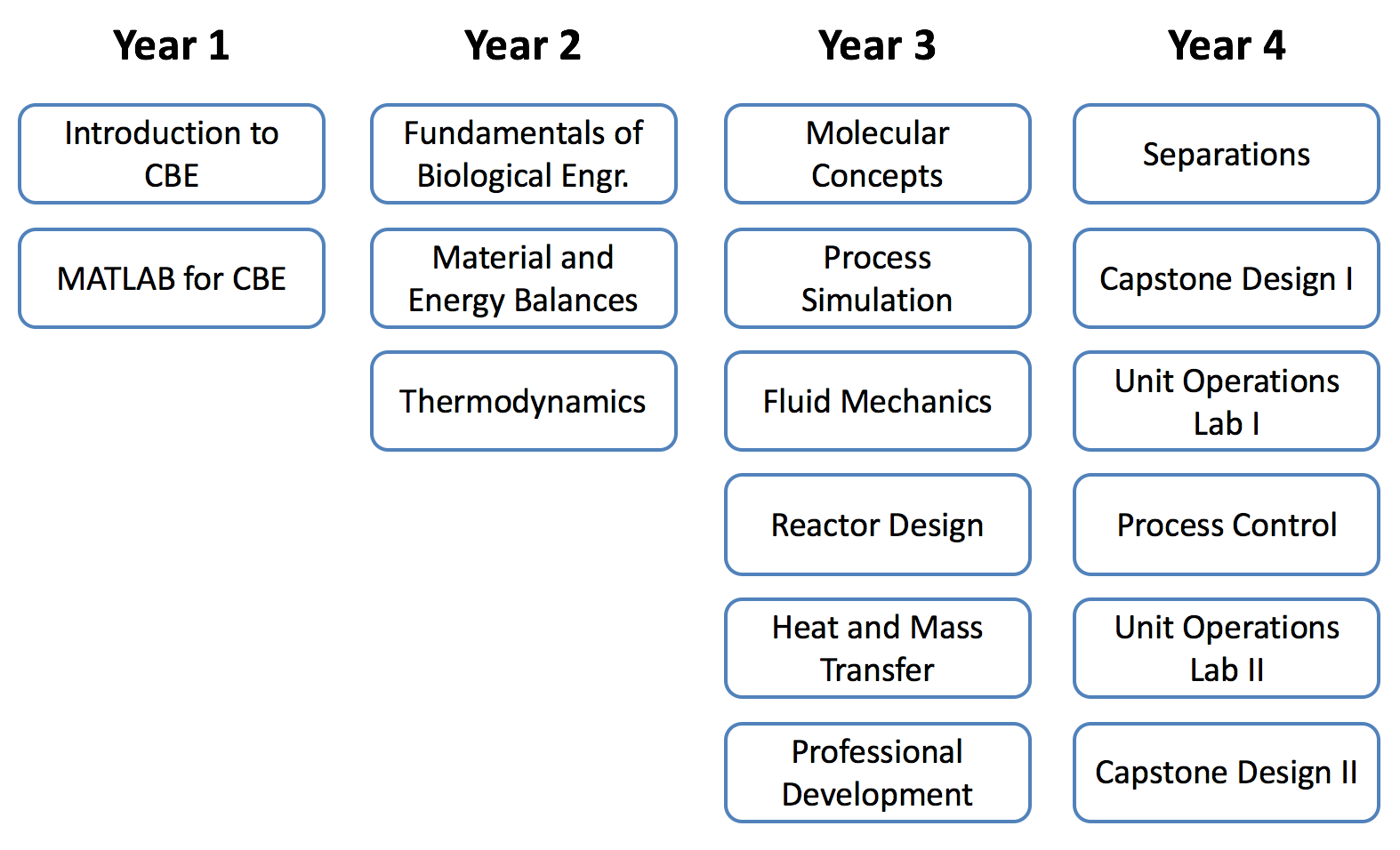
Now, let’s look at all of the CBE and required technical courses and see how they fit together.
In this graphic, progression through the sequence is from top to bottom (i.e., Year 1: Fall semester courses are shown in the uppermost row).
highlighted box: requires a C or better
solid lines: prerequisite
dashed lines: co-requisite
Opportunities outside of the classroom¶
Research with a faculty member in CBE or in any other department at CSU. Check out the research activities in CBE and look at other departments’ websites to get an idea of who is doing what across campus. Politely reach out to the appropriate faculty member if you have an interest.
CBE-related student organizations:
National Science Foundation REU (Research Experience for Undergraduates)
Internships and co-ops. Stop by the Engineering Success Center for details.