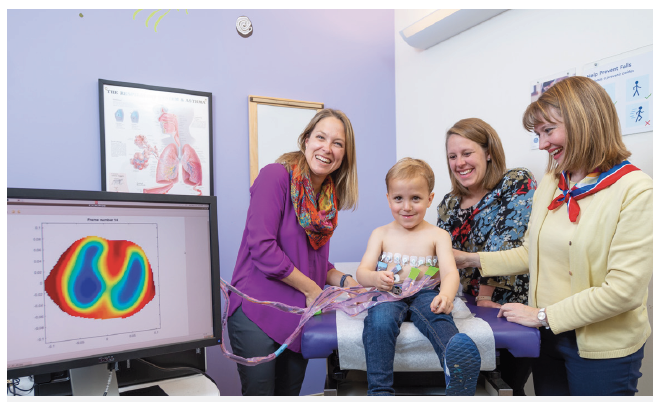
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is the most common fatal genetic disease in the United States, and its progression is characterized by a cumulative decline in lung function. Disease management and treatment decisions are currently guided by the results of pulmonary function tests (PFT’s) to assess lung function and CT scans to assess lung structure.
However, very young children are unable to perform PFT’s, and CT scans expose patients to ionizing radiation, limiting its frequency of use. Electrical impedance tomography (EIT) is a non-ionizing real-time imaging technique that has been shown to provide regional pulmonary information and is safe for patients of all ages.
This study uses EIT to detect changes in lung structure and function longitudinally in CF patients. The outputs of this study may improve the care of patients with CF and other chronic lung diseases.
Collaborators:
Children’s Hospital Colorado and University of Albany.

Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is the most common morbidity of prematurity with over 10,000 infants diagnosed each year in the United States and affecting up to 40% of infants born before 29 weeks gestational age.
Electrical impedance tomography has been shown to provide regional pulmonary information and is safe for patients of all ages. This work is to detect changes in the lungs of BPD patients pre and post changes in ventilation strategy and at key time points in their development to assess EIT’s potential to guide the clinician in the treatment strategy in infants with BPD.
Collaborators:
Children’s Hospital Colorado, Stanford University, University of Albany, and GE Healthcare.
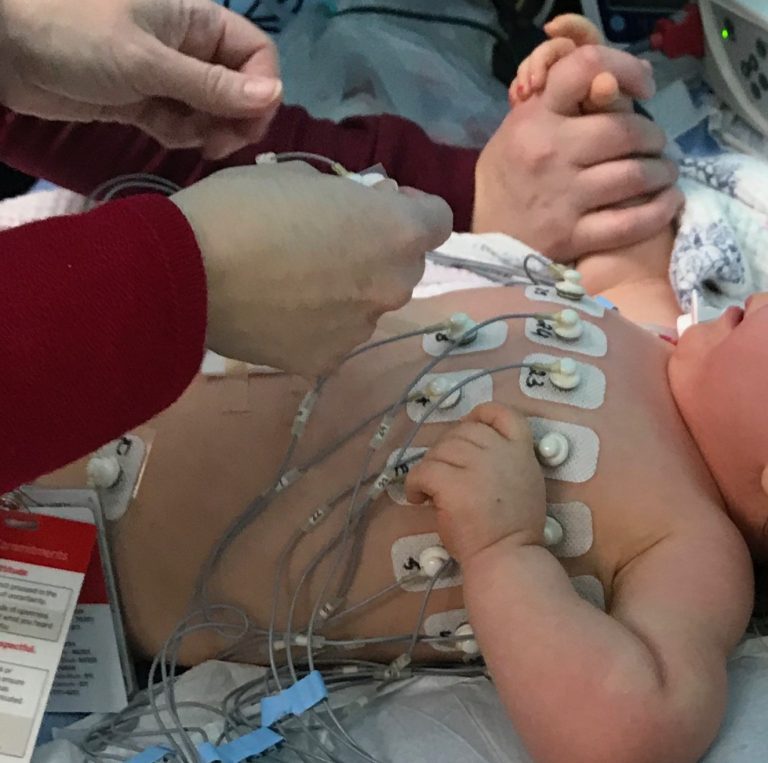
Intubating newborns for mechanical ventilation is challenging due to their size and delicate nature. Unfortunately, nearly 40% of initial intubation attempts result in accidental misplacement of the endotracheal tube in the esophagus instead of the trachea or incorrectly in the trachea or bronchus, and it is critical to detect such tube misplacement promptly. This work combines deep learning Simultaneous Multi Source Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT)-based confirmation of tube placement with EIT images of lungs being ventilated, resulting in a real-time, closed-loop system for tube placement detection and ventilation imaging.
Collaborators:
Stanford University and GE Healthcare

Pulmonary vein stenosis (PVS) is a complex congenital heart disease that requires repeated catheterization interventions for its treatment.
In this study we aimed to determine the feasibility of EIT to evaluate degree and severity of PVS before and after catheter-based interventions using the ACT 5 system. We found that the subject-based evaluation of EIT correlates to the severity and sidedness of the veins involved.
Collaborators:
Children’s Hospital Colorado and University of Albany.
Real-time EIT pulmonary imaging for infants requiring ventilatory therapy, NIH/NICHD, Mueller PI
Real-time noninvasive visualization of endotracheal tube placement and 3D lung monitoring in infants with electrical impedance tomography, NIH/NIBIB, Mueller PI