 |
ResearchMajor External Research GrantsResearch in CSU Electromagnetics Lab PhD, MS, REU Students ATMC Telecom. Lab, UMD Research at CU and U of Belgrade EM and Engineering Education Research Graduate and Undergraduate Research Assistantships available on NSF, DoD, and other grants. |
Major External Research Grants
Active grant funding in 2017:
- Total Active as PI: $1.4M
- Total Active as Co-PI: $3.3M
- Indirect cost generation in the top five in the ECE Department at CSU. ECE Department is one of the departments with highest external research funding and expenditures at Colorado State University, https://www.engr.colostate.edu/ece/research/.
Active grant funding in 2016:
- Total Active as PI: $1,913,604.00
- Total Active as Co-PI: $3,231,636.00
Grant “Novel AI-Based Multiview Detailed Classification, AI-Enabled 3D Shape Reconstruction, Multicamera Instrumentation, and Comprehensive Analysis & Profiling of Snowflakes and Snowfall,” from the National Science Foundation, Geosciences Directorate, Atmospheric and Geospace Sciences (AGS) Division, Physical and Dynamic Meteorology (PDM) Program, unsolicited grant, PI: Branislav Notaros (single-PI grant), start date April 15, 2025, end date March 31, 2028, $498,976, Award No. AGS-2445598 (Program Director: Dr. Nicholas Anderson).
Grant “Revolutionizing Simulation-Based Design: Adaptive Anisotropic Multiscale Computational Methods for Electromagnetics and Engineering,” from the National Science Foundation, Engineering Directorate, Electrical, Communications and Cyber Systems (ECCS) Division, Communications, Circuits, and Sensing Systems (CCSS) Program, unsolicited grant, PI Branislav Notaros (single-PI grant), start date August 1, 2024, end date July 31, 2027, $450,000, Award No. 2414473 (Program Director: Dr. Jenshan Lin).
Grant “CDS&E: ECCS: Accurate and Efficient Uncertainty Quantification and Reliability Assessment for Computational Electromagnetics and Engineering,” from the National Science Foundation, Engineering Directorate, Electrical, Communications and Cyber Systems (ECCS) Division, Computational and Data‐Enabled Science and Engineering (CDS&E) Program, PI Branislav Notaros (single-PI grant), start date June 15, 2023, end date May 31, 2026, $420,000, Award No. 2305106 (Program Director: Dr. Jenshan Lin).
Contract “RF Analysis and Validation Engineering Software (RAVEnS),” from the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL), Applied Research Associates (ARA), PI: Branislav Notaros (single-investigator contract), start date July 1, 2020, end date June 30, 2025, $1,000,000, Contract No. FA8650-20-C-1132.
Grant “Novel Integrated Characterization of Microphysical Properties of Ice Particles Using In-Situ Field Measurements and Polarimetric Radar Observations,” from the National Science Foundation, Geosciences Directorate, Atmospheric and Geospace Sciences (AGS) Division, Physical and Dynamic Meteorology (PDM) Program, unsolicited grant, PI: Branislav Notaros, co-PI: V. Bringi, start date October 1, 2020, end date September 30, 2026, $647,003, Award No. AGS- 2029806 (Program Director: Dr. Nicholas Anderson).
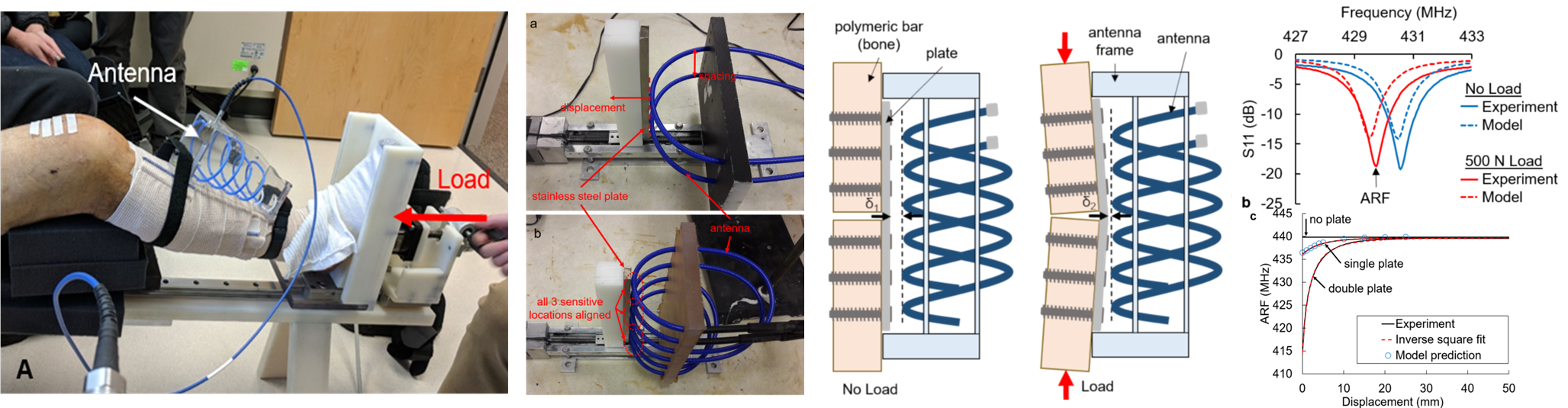
Grant “A Telemedicine Approach for Monitoring Fracture Healing Via Direct Electromagnetic Coupling,” from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), NIH R21 grant, PI: Christian Puttlitz, Co-PIs: Kevin Labus and Branislav Notaros, and Subcontract to UC Denver, start date March 1, 2020, end date February 28, 2024, $351,322 (B. Notaros part: $93,835), Grant No. 1R21AR077323.
Grant “Direct Electromagnetic Coupling for Diagnostic Prediction of Fracture Healing,” from the Office of Economic Development and International Trade (OEDIT), State of Colorado, PI: Christian Puttlitz, Co-PIs: Kevin Labus, Branislav Notaros, and Jeremiah Easley, start date March 1, 2020, end date February 28, 2021, $170,000.
Grant “Novel RF Volume Coils for High and Ultra-High Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scanners,” from the National Science Foundation, Engineering Directorate, Electrical, Communications and Cyber Systems (ECCS) Division, Communications, Circuits, and Sensing Systems (CCSS) Program, unsolicited grant, PI Branislav Notaros (single-PI grant), start date September 1, 2018, end date August 31, 2024, $370,000, Award No. ECCS-1810492 (Program Director: Dr. Jenshan Lin).
Grant “Development of Uncertainty Quantification and Design Approaches and Solutions,” from the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL), CREATE SENTRi, Riverside Research Institute, PI: Donald Estep (Statistics Department), co-PI: Branislav Notaros (B. Notaros part: 65%), co-PI: Troy Butler (subcontract to University of Colorado Denver), start date September 19, 2016, end date September 18, 2021, $744,882.
Grant "CPS: Synergy: Collaborative Research: Enabling Smart Underground Mining with an Integrated Context-Aware Wireless Cyber-Physical Framework,” from the National Science Foundation, Engineering Directorate, Electrical, Communications and Cyber Systems (ECCS) Division, Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) Program, PI: Sudeep Pasricha, co-PI: Branislav Notaros, start date October 1, 2016, end date September 30, 2020, CSU part: $412,500, Award No. ECCS-1646562.
Grant “Toward a More Statistically Robust, Generalized Process Evaluation Framework of Bin and Bulk Microphysics in Winter Precipitation Using NASA GV and GPM-DPR Data,” from NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration), Science Mission Directorate, Earth Science, Precipitation Measurement Missions (PMM), PMM Science Team, PI: Branislav Notaros, co-PIs: V. N. Bringi and Andrew Newman, start date March 1, 2016, end date August 31, 2020, $240,000, Award No. NNX16AE43G.
Grant “IUSE Revolutionizing Engineering Departments (RED): Revolutionizing Roles to Reimagine Integrated Systems of Engineering Formation (R2E2 – Revolutionary Redesign of Engineering Education),” from National Science Foundation, Directorate of Engineering, Division of Engineering Education and Centers (EEC), PI: Anthony Maciejewski, ECE Dept. Head; B. Notaros is Senior Personnel on this grant; start date July 1, 2015, end date June 30, 2021, $1,988,663, Award No. EEC 1519438.
Grant “Advanced Comprehensive Analysis of Rain Drop Shapes, Oscillation Modes, and Fall Velocities Using High-Resolution Surface Disdrometers, Polarimetric Radar, and Numerical Models,” from the National Science Foundation, Geosciences Directorate, Atmospheric and Geospace Sciences (AGS) Division, Physical and Dynamic Meteorology (PDM) Program, unsolicited grant, PI: V. Bringi, co-PI: Branislav Notaros, start date January 1, 2015, end date December 31, 2019, $530,342, Award No. AGS-1431127.
Grant “Accurate Characterization of Winter Precipitation Using Multi-Angle Snowflake Camera, Visual Hull, Advanced Scattering Methods, and Polarimetric Radar,” from the National Science Foundation, Geosciences Directorate, Atmospheric and Geospace Sciences (AGS) Division, Physical and Dynamic Meteorology (PDM) Program, unsolicited grant, PI Branislav Notaros, co-PI: V. Bringi, start date December 1, 2013, end date November 30, 2018, $607,967, Award No. AGS-1344862.
Grant “Treatment Methodologies for Radiofrequency (RF) Injuries,” subcontract RF Applicator System Development, from Wyle Laboratories, Inc./USAF School of Aerospace Medicine (USAFSAM)/AFOSR, subcontract PI Branislav Notaros (CSU PI Thomas Johnson, Department of Environmental and Radiological Health Sciences), start date September 4, 2013, end date December 1, 2014, $71,497.
Grant “Suppression of Wind Turbine Clutter from Radar Data,” from Matrix Research, Inc./Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFOSR), Small Business Technology Transfer (STTR) Program – Phase I, Margaret Cheney, V. Chandraskar, Branislav Notaros, start date October 15, 2013, end date January 14, 2014, $90,000.
Grant “Collaborative Research: Electromagnetic Field Profile Design for Next-Generation Travelling-Wave MRI,” from the National Science Foundation, Engineering Directorate, Electrical, Communications and Cyber Systems (ECCS) Division, Communications, Circuits, and Sensing Systems (CCSS) Program, unsolicited grant, PI Branislav Notaros, start date July 1, 2013, end date June 30, 2019, CSU part: $248,000, Award No. ECCS-1307863.
Grant “Diakoptic Approach to Modeling and Design of Complex Electromagnetic Systems,” from the National Science Foundation, Engineering Directorate, Electrical, Communications and Cyber Systems (ECCS) Division, Integrative, Hybrid and Complex Systems (IHCS) Program, unsolicited grant, PI Branislav Notaros (single-investigator grant), start date May 1, 2010, end date April 30, 2016, $404,000, Award No. ECCS-1002385.
Grant “Analysis of Structures for 3-D ALERT,” subcontract from the University of Colorado at Boulder, Phase 0 DARPA grant, collaboration of CU Boulder (Prof. Zoya Popovic), CSU, and BAE Systems. CSU budget $20,000, start date February 23, 2007, end date March 31, 2007. CSU PI Branislav Notaros.
Grant “Efficient Higher Order Techniques for Electromagnetic Modeling and Design of Photonic Crystal Structures,” from the National Science Foundation, Engineering Directorate, Electrical, Communications and Cyber Systems (ECCS) Division, Integrative, Hybrid and Complex Systems (IHCS) Program, unsolicited grant, PI Branislav Notaros (single-investigator grant), start date September 1, 2006, end date August 31, 2011, $410,396, Award No. ECCS-0650719.
Grant “Textile Based Carbon Nanostructured Flexible Antenna,” from the National Textile Center (NTC), Competency: Materials, B. Notaros is a co-PI, collaborative project with colleagues in the ECE Department and Materials and Textiles Department at UMass Dartmouth and Rennselaer Polytechnic Institute, start date June 1, 2006, end date May 31, 2009, $155,000 per year, Project ID: M06-MD01.
Grant “Higher-Order Finite Element-Moment Method Modeling Techniques for Conformal Antenna Applications,” from the National Science Foundation, Engineering Directorate, Electrical, Communications and Cyber Systems Division, Electronics, Photonics, and Device Technologies (EPDT) Program, unsolicited grant, PI Branislav Notaros (single-investigator grant), start date September 1, 2003, end date August 31, 2009, $249,417, Award No. ECCS-0647380.
Grant “Large-Domain Hybrid Moment Method–Physical Optics Techniques for Efficient and Accurate Electromagnetic Modeling of Cars and Aircraft over a Wide Range of Frequencies,” from the National Science Foundation, Engineering Directorate, Electrical and Communications Systems Division, EPDT Program, unsolicited grant, PI Branislav Notaros (single-investigator grant), start date September 1, 2001, end date August 31, 2005, $192,000, Award No. ECS-0115756.
NSF Foundation Coalition grant, project “Electromagnetics Concept Inventory” – Branislav Notaros, National Science Foundation, Engineering Directorate, Engineering Education and Centers Division, start date June 1, 2000, end date August 31, 2003, approx. $70,000, Award No. EEC-9802942.
Research in the Electromagnetics Laboratory
Eng B110, Colorado State University
(Director Branislav Notaros)
Research expertise, interests, contributions, initiatives, and future plans of the Electromagnetics Laboratory at Colorado State University, ECE Department, are in the area of electromagnetics, and in its crossings with other areas of science and engineering. Our current research activities span a very broad range of exciting and emerging topics in computational electromagnetics; modeling and numerical methods; higher order CEM methodologies and tools; antennas; scattering; AI and machine learning in computational EM, remote sensing, and medical imaging and diagnostics; cyber-physical systems; error estimation; adaptive model refinement; uncertainty quantification; atmospheric/meteorological electromagnetics; radar meteorology; characterization of snow and rain; surface and radar precipitation measurements; image processing; RF/optical instrumentation development; bioelectromagnetics; RF design for magnetic resonance imaging at high and ultrahigh magnetic fields; direct electromagnetic coupling system for orthopaedic diagnostics; telemedicine system for orthopaedic applications; and electromagnetics education.
While these topics and applications are really “all over” science and engineering, we focus on the strong interweaving common thread among all of them – electromagnetics.

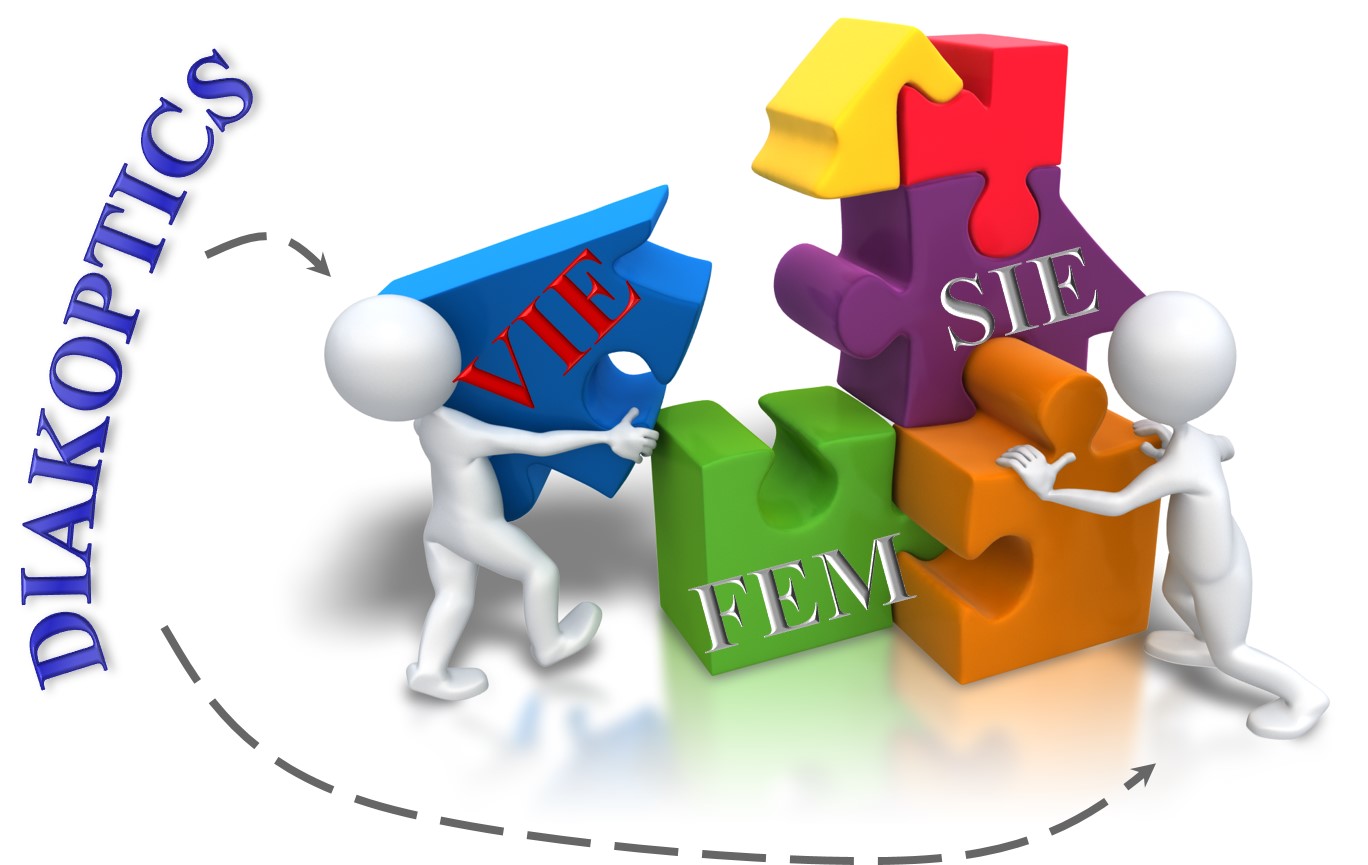
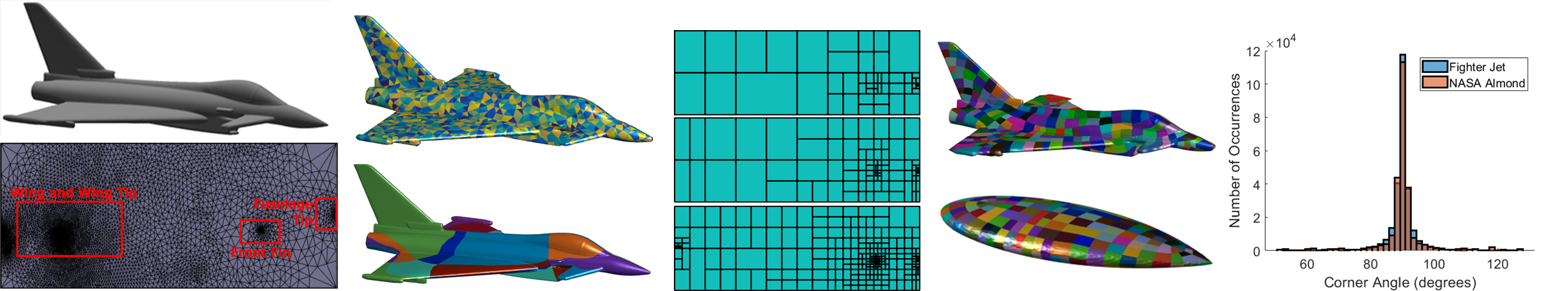
Our main contributions to computational electromagnetics (CEM) are in higher order CEM techniques based on the method of moments (MoM), surface integral equation (SIE) approach, volume integral equation (VIE) formulation, finite element method (FEM), ray tracing (RT), physical optics (PO), domain decomposition method (DDM), diakoptics, hybrid CEM methods, adjoint methods, a posteriori error estimation, adaptive model refinement, uncertainty quantification, sensitivity analysis, and general surface meshing methods, as applied to modeling and design of antennas, scatterers, and RF/microwave and optical devices and systems.

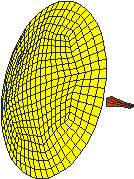
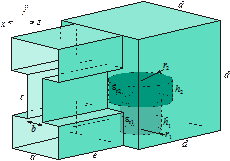
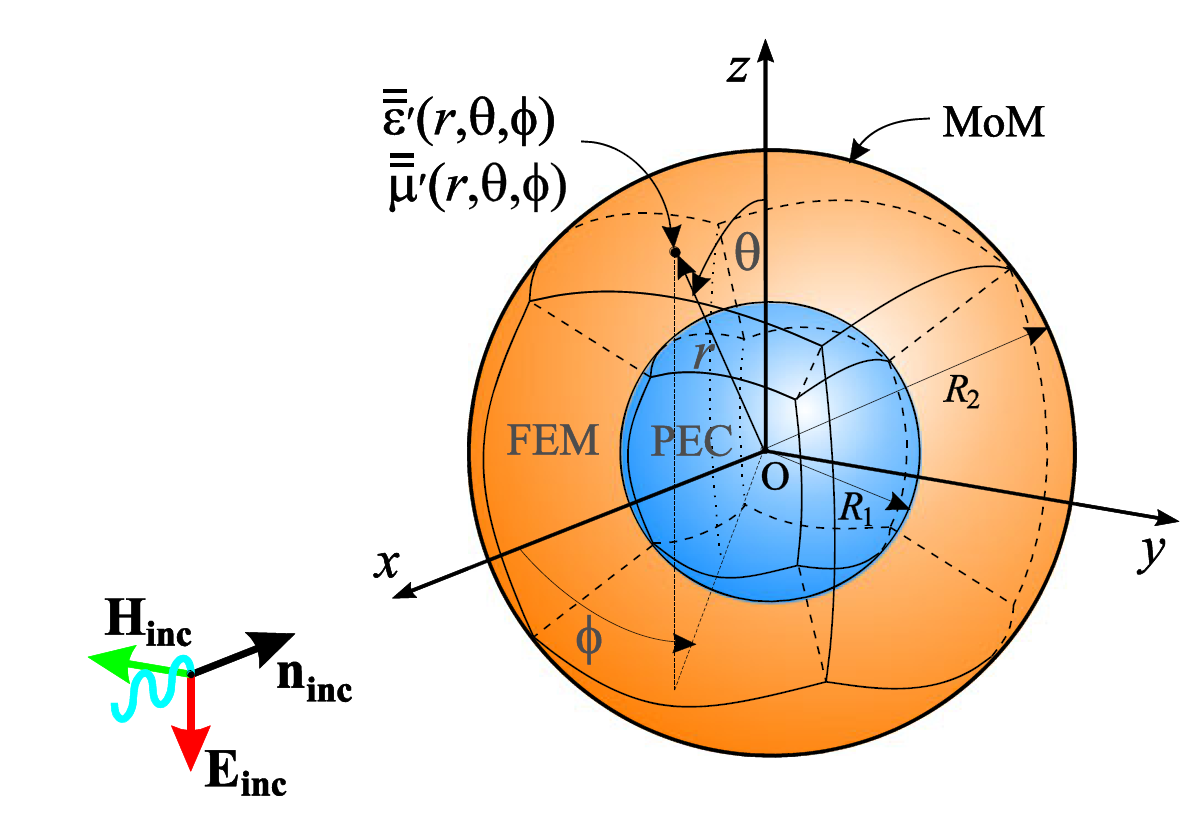
In addition to higher order, large (up to few wavelengths in each dimension) elements (large-domain modeling), a mixture of low-to-high-order, small-to-large elements is possible in the same CEM model. Our elements and basis functions are hierarchical and suitable for p- and hp-refinements. We are also developing and advancing all sorts of hybrid higher order CEM methods, e.g., FEM-SIE, VIE-SIE, MoM-PO, SIE-FEM-diakoptics, SIE-VIE-diakoptics, and so on.

Some current projects include:
- revolutionizing simulation-based design: adaptive anisotropic multiscale computational methods for electromagnetics and engineering;
- computational and data-enabled science and engineering: accurate and efficient uncertainty quantification (UQ) and reliability assessment for computational electromagnetics and engineering;
- advances of AI and machine learning as applied to computational EM, remote sensing, and medical imaging and diagnostics;
- error estimation, adaptive model refinement, and uncertainty quantification for RF Analysis and Validation Engineering Software (RAVEnS);
- development of UQ and design approaches and solutions for CREATE/SENTRi;
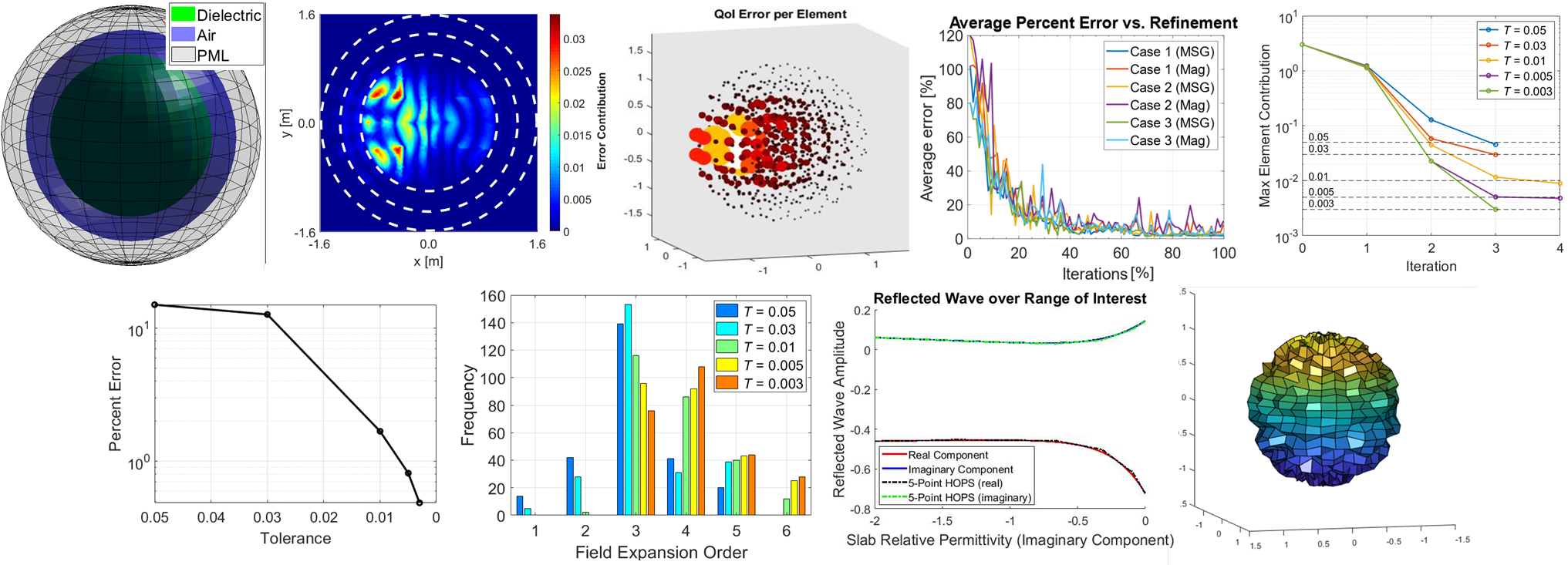
- adjoint-based error estimation and control, adaptive model refinement, sensitivity analysis, and accelerated high-dimensional UQ;
- novel synergistic approach to fully adaptive error control (both deterministic and statistical) and UQ for reliability assessment in engineering applications and EM systems and devices;
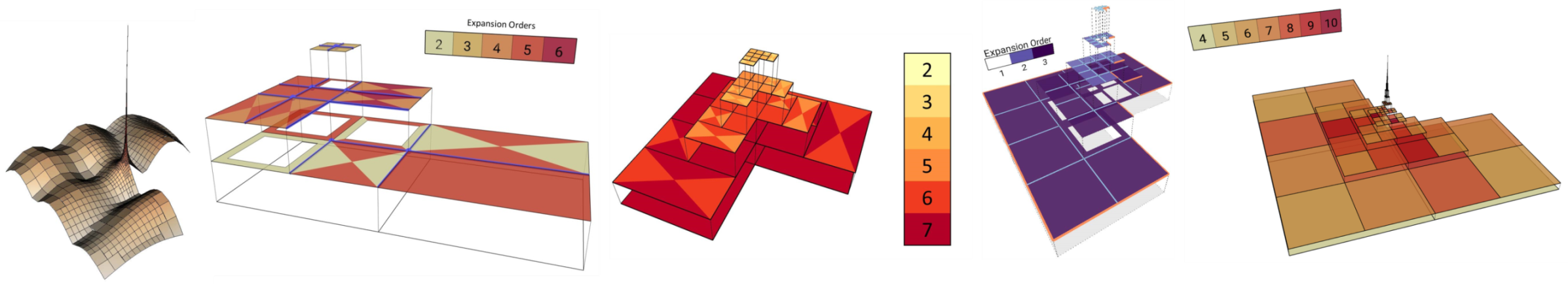
- refinement-by-superposition approach to adaptive fully anisotropic hp-refinement in computational electromagnetics, with theoretically guaranteed exponential convergence of solutions in all cases;
- general surface meshing in CEM using discrete surface Ricci flow and iterative adaptive refinement;
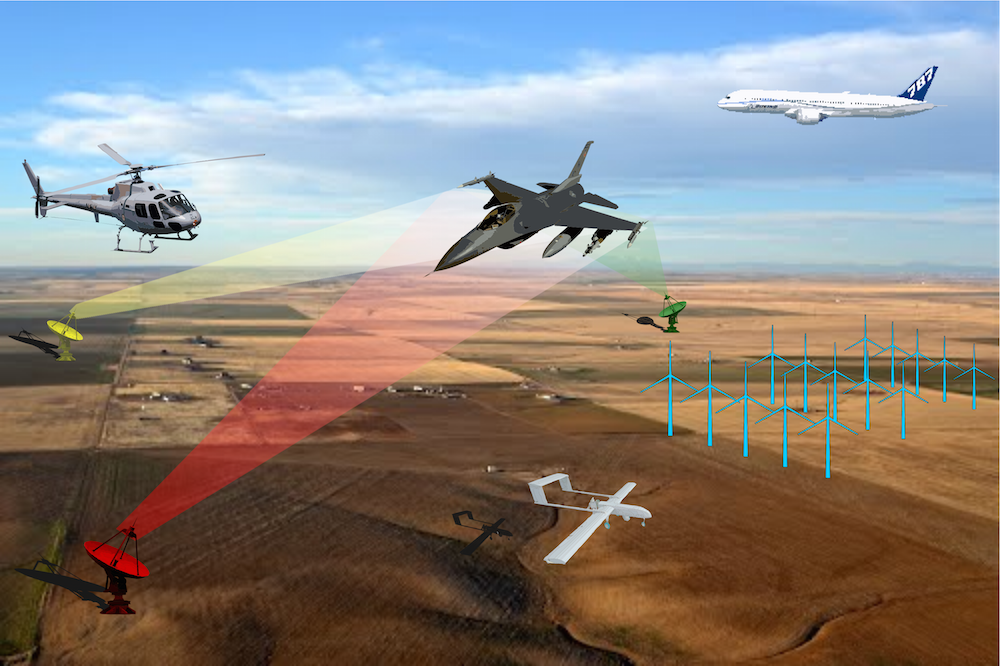
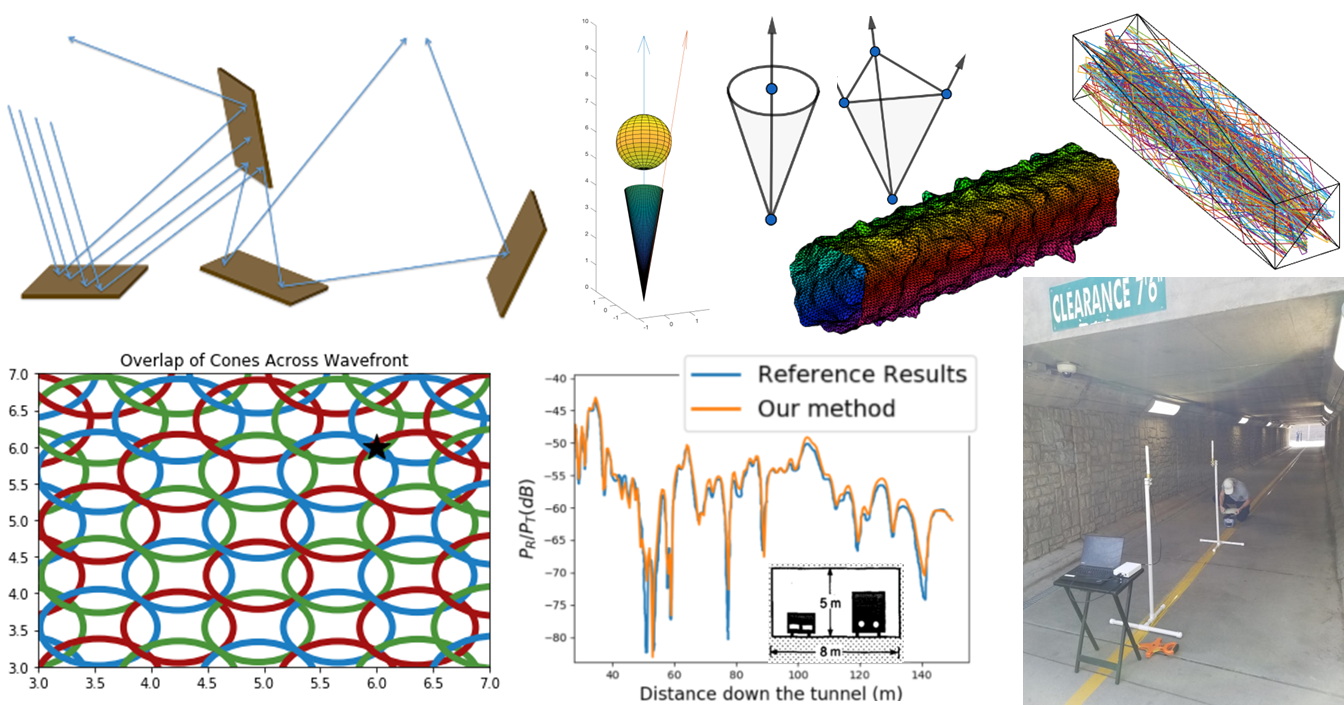
- novel shooting and bouncing ray tracing techniques for indoor and outdoor propagation modeling: advancing accuracy and parallel GPU optimization;
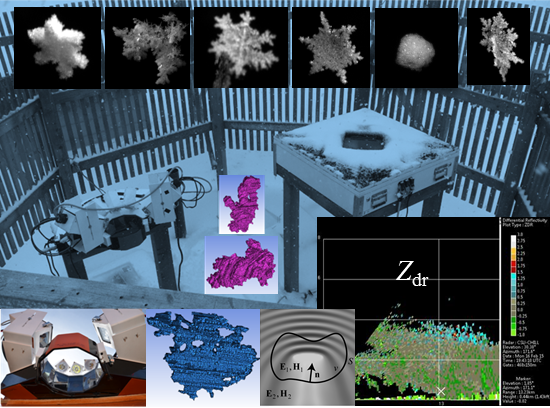
- novel integrated characterization of microphysical properties of ice particles using in-situ field measurements and polarimetric radar observations;
- accurate characterization of winter precipitation using multi-angle snowflake camera, visual hull, advanced scattering methods, and polarimetric radars;
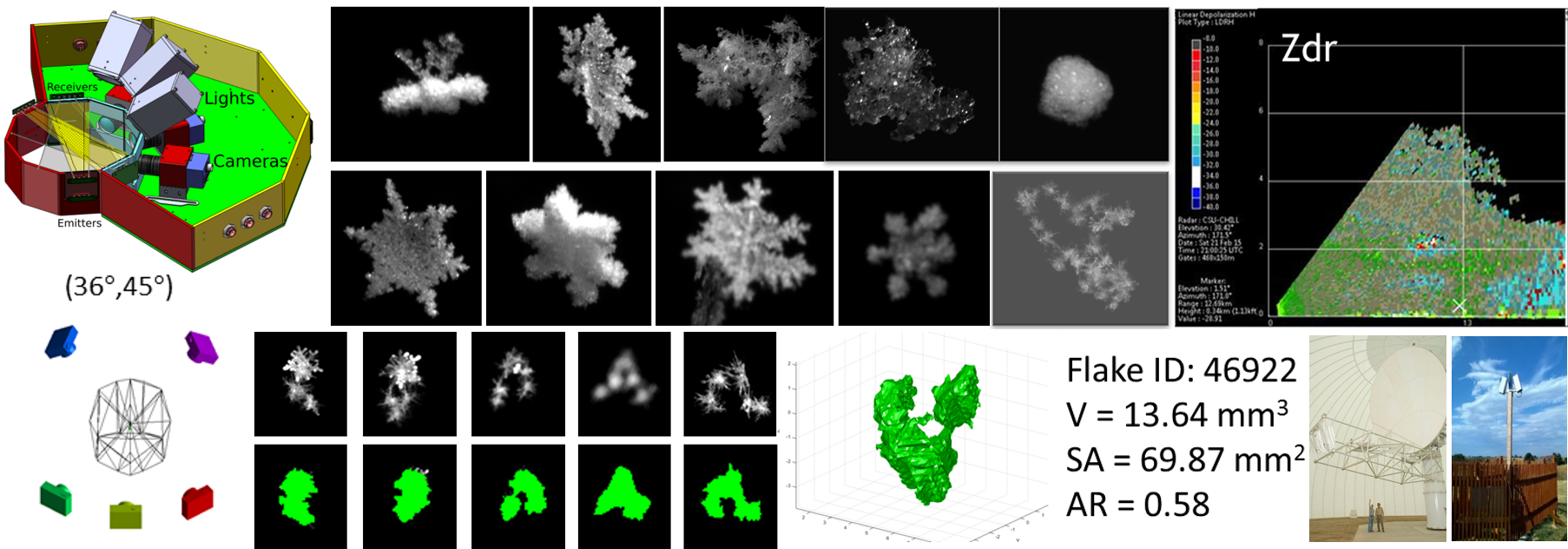

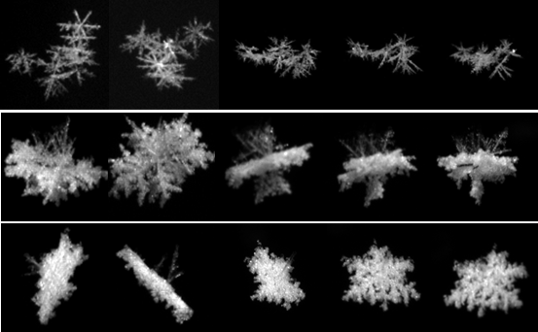
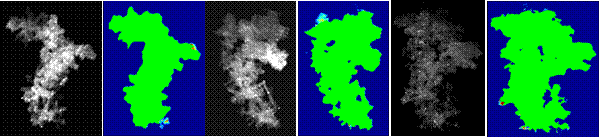
- AI-enabled analysis, characterization, classification, and profiling of winter precipitation and snow particles based on multicamera instruments, image processing, and machine learning methodologies;
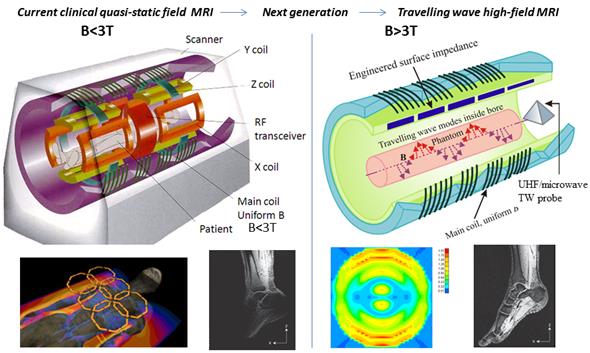
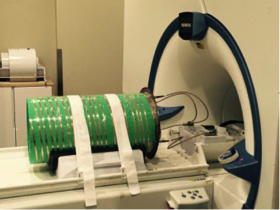
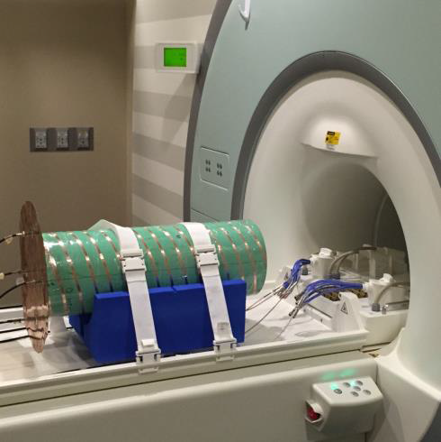
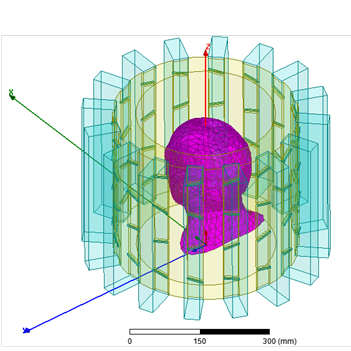
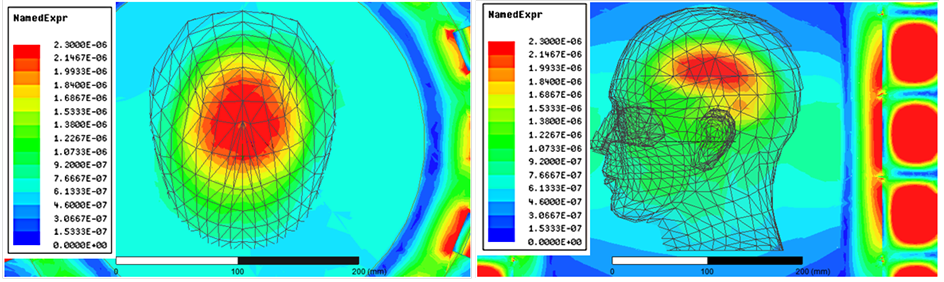
- novel RF volume coils (antennas) for next-generation high and ultrahigh field (B0 ≥ 3T) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanners;
- integrated design of exposure and excitation of EM RF fields for traveling-wave MRI at high and ultrahigh magnetic fields;
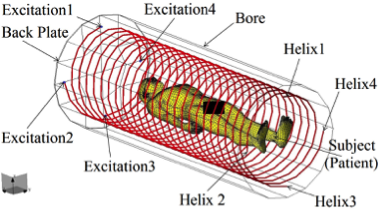
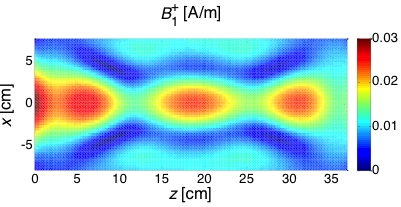
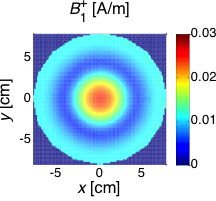
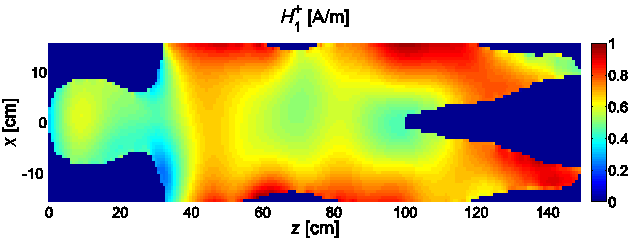
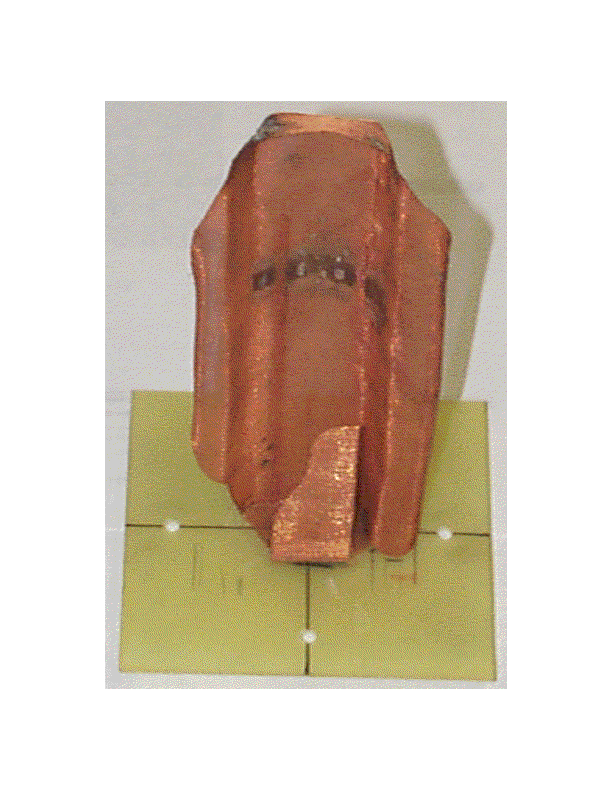
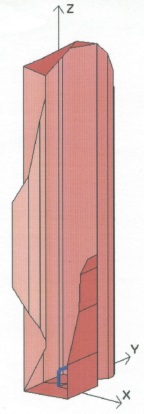
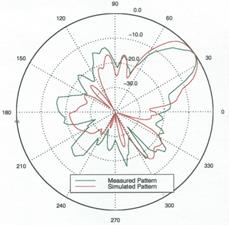
Quadrifilar Helical Antenna as a Whole-Body Traveling-Wave RF Coil for 3T and 7T MRI
RF Excitation in 7 Tesla MRI Systems Using Monofilar Axial-Mode Helical Antenna
Long and Short Monofilar and Quadrifilar Helical Antenna RF Coils at 7 T
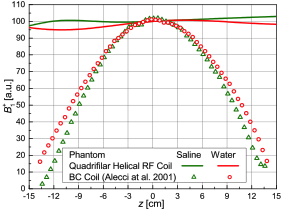
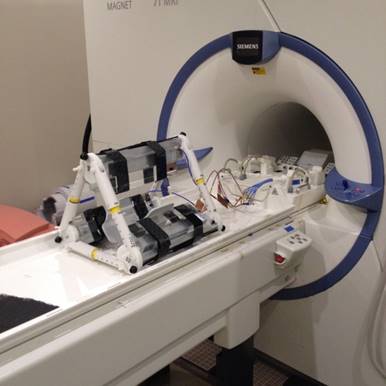
Subject-loaded quadrifilar helical-antenna RF coil with high B1+ field uniformity and large FOV for 3-T MRI - direct electromagnetic coupling (DEC) system for human orthopaedic fracture-healing diagnostics;
- telemedicine system for orthopaedic patient self-testing and data transmission;
- advanced comprehensive analysis of rain drop shapes, oscillation modes, and fall velocities using high-resolution surface disdrometers, polarimetric radar, and numerical models;
Measurement and Analysis of Rain Precipitation at MASCRAD Instrumentation Site in Colorado
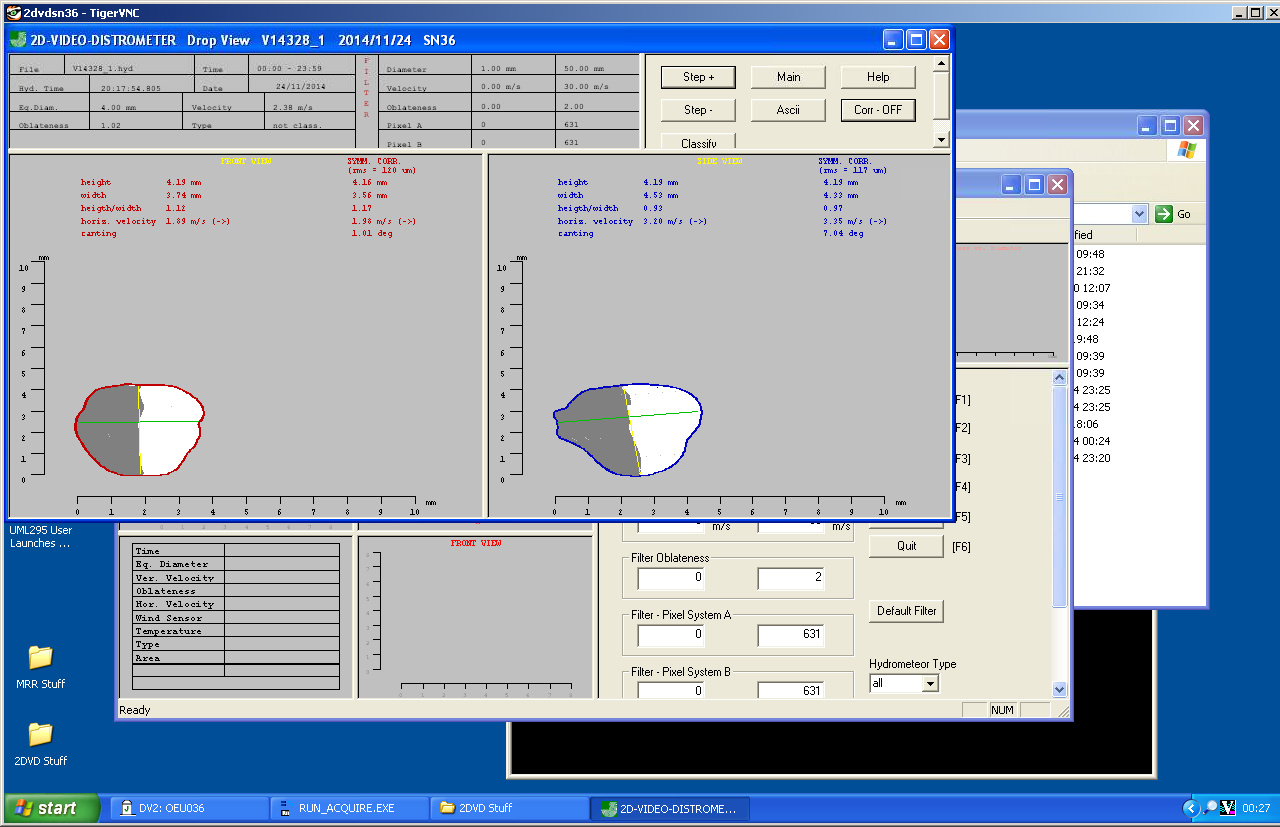
Towards Completing the Rain Drop Size Spectrum: Case Studies Involving 2D-Video Disdrometer, Droplet Spectrometer, and Polarimetric Radar Measurements
DPWX/Microburst winds and melting hail at the Easton Airport field site: 9 July 2015
Investigating rain drop shapes, oscillation modes, and implications for radiowave propagation
Large Raindrops Against Melting Hail: Calculation of Specific Differential Attenuation, Phase and Reflectivity
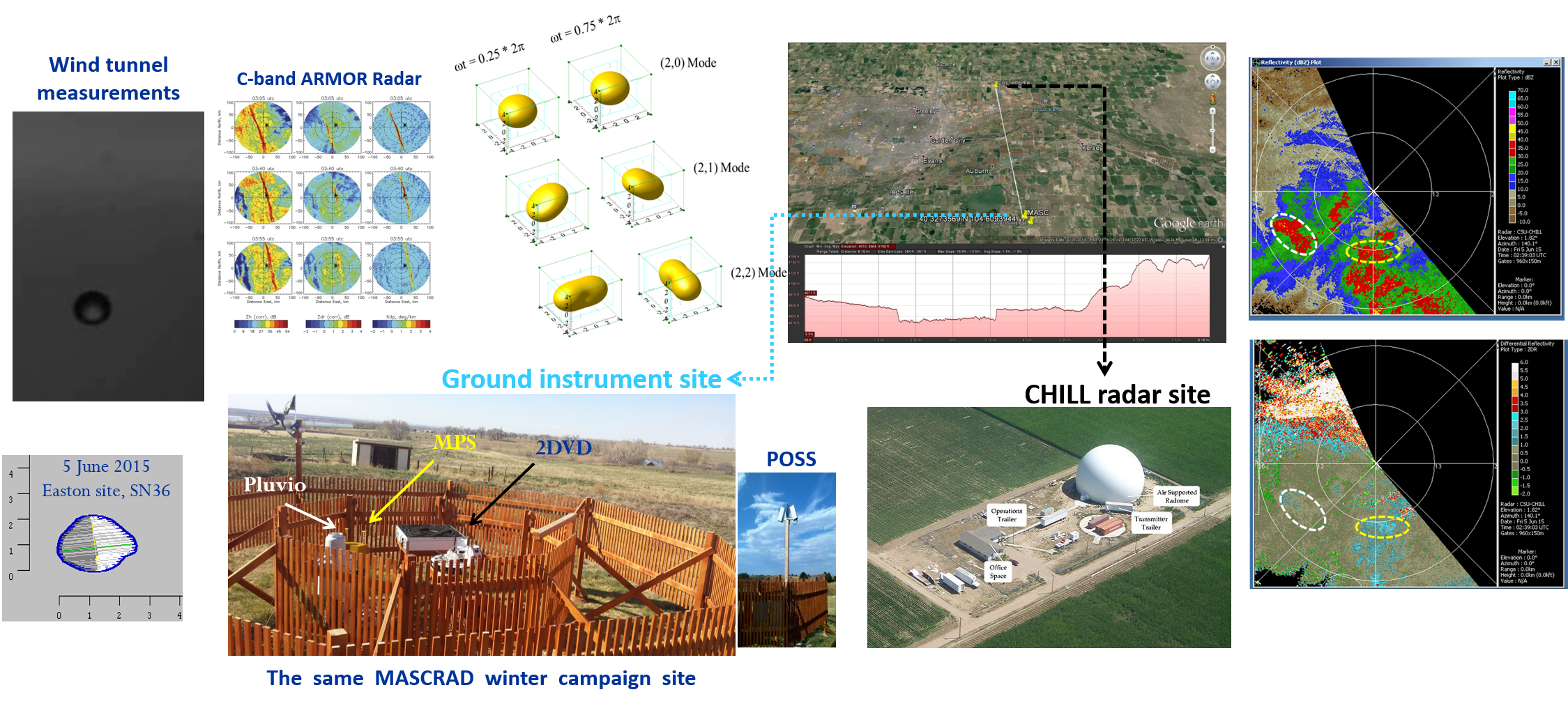
- AI-enabled data-driven machine learning-based approach to accelerate MoM, FEM, and related variational methods by predicting macro basis functions;
- fast scalable higher order direct algorithms for large and complex problems in computational sciences and engineering;
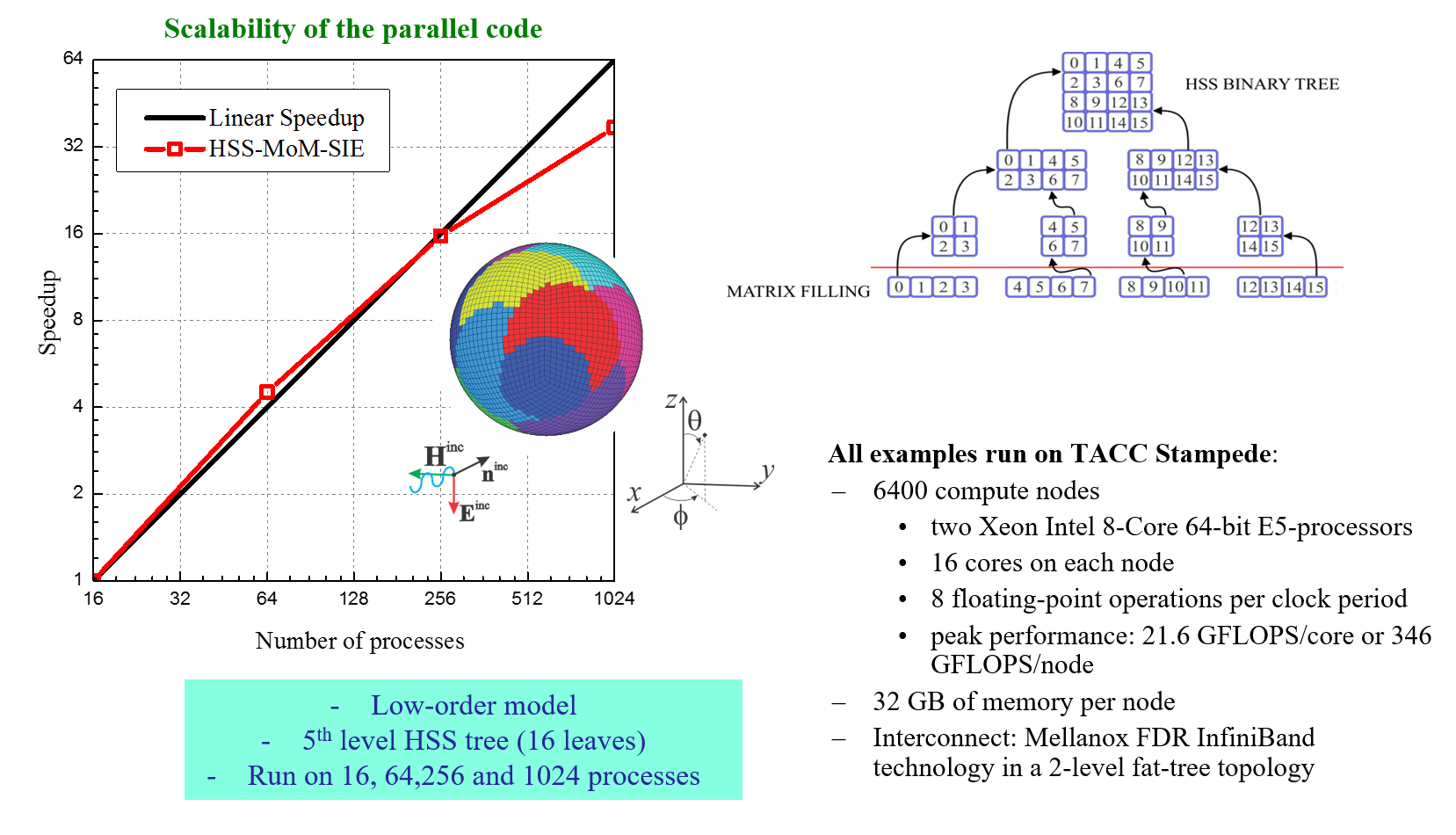
- hierarchical matrix methods for extreme-scale parallel computing on leading-edge HPC platforms;
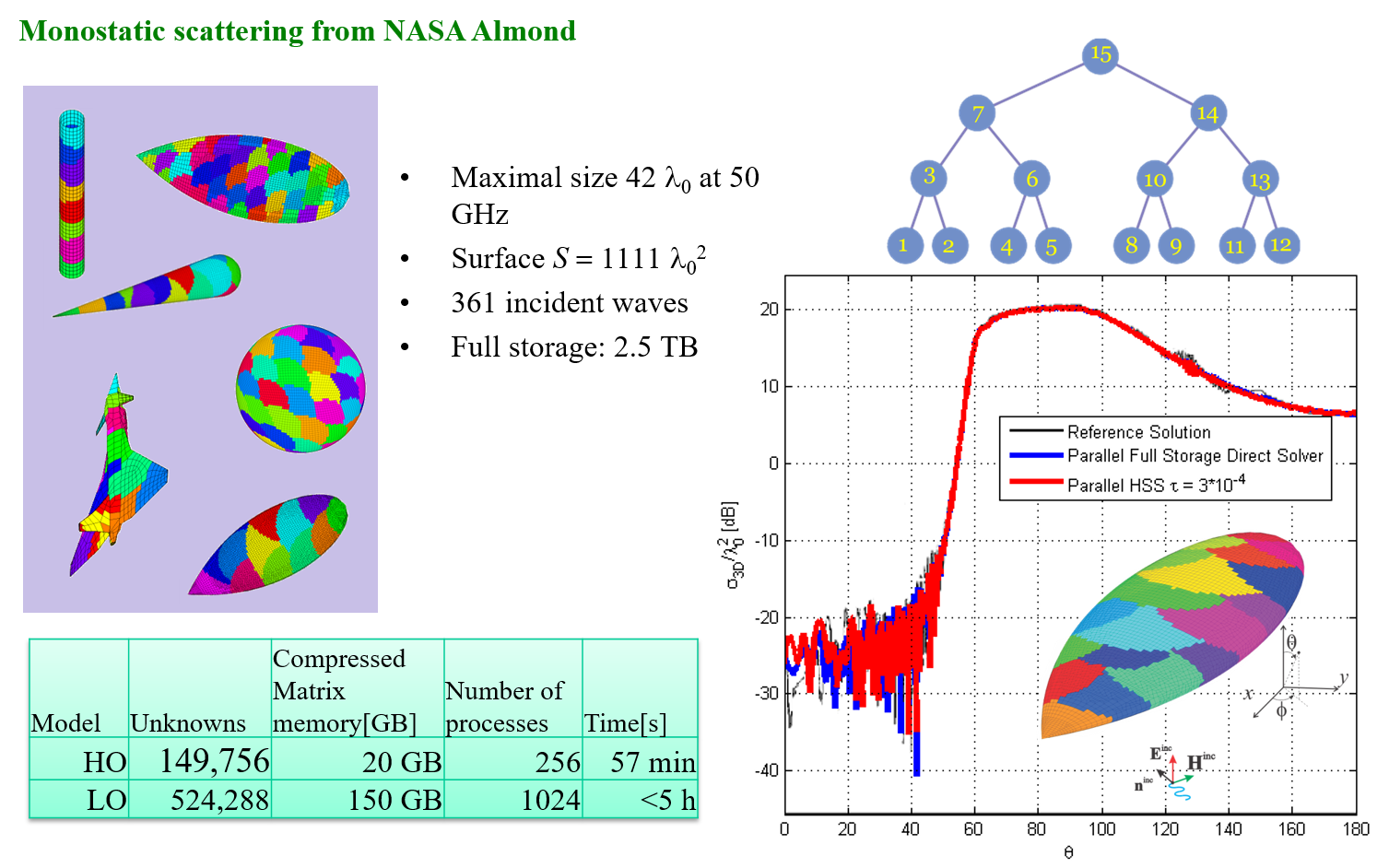
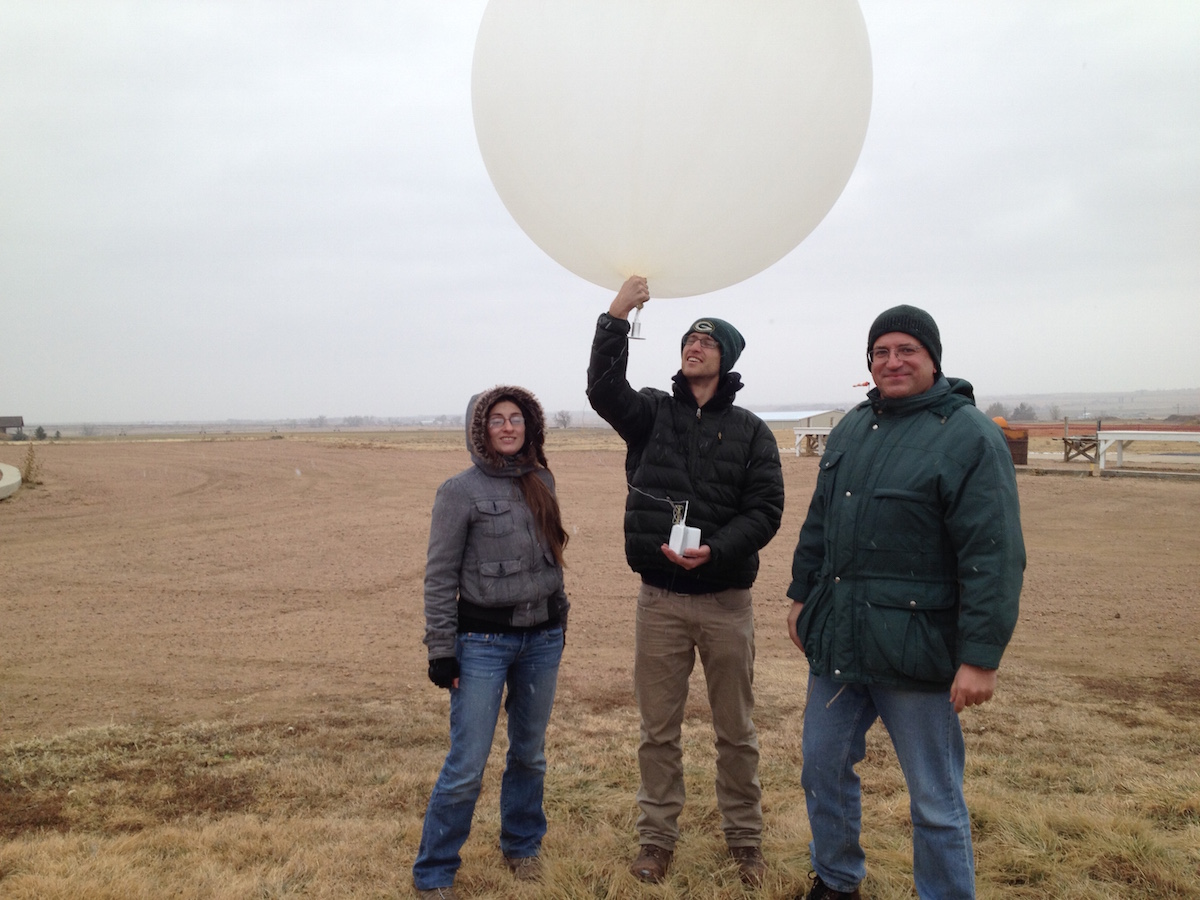
- observational analysis, modeling, and development of a statistically robust, generalized process evaluation framework of bin and bulk microphysics in winter precipitation using NASA GV and GPM-DPR data;
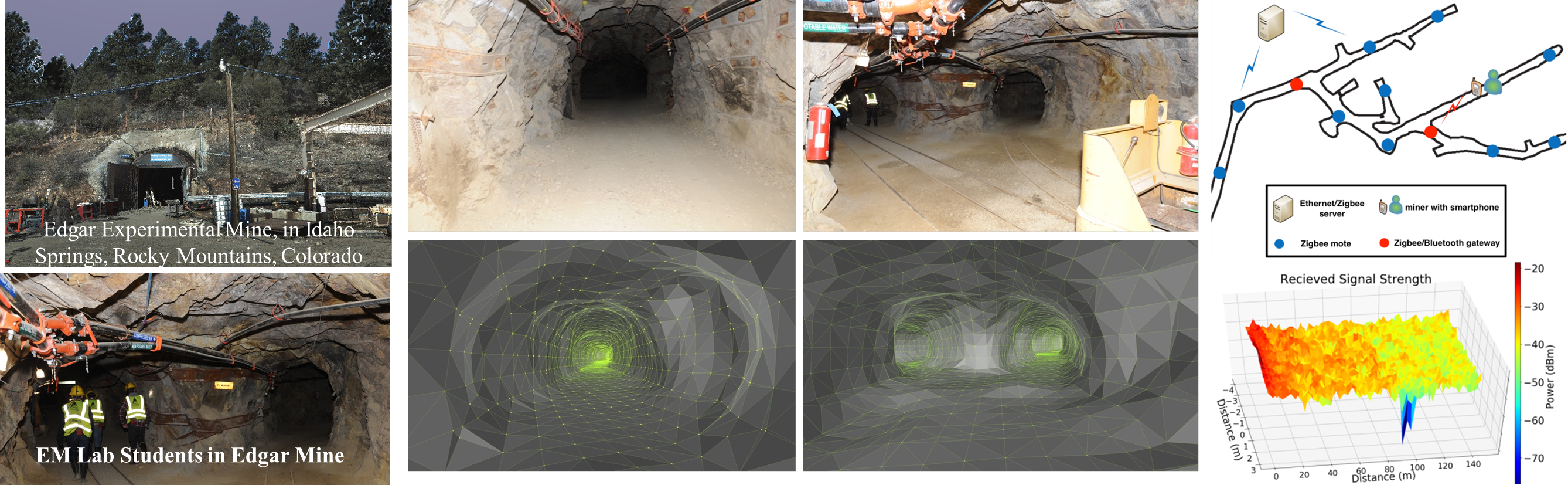
- cyber-physical systems: modeling and measurements of EM propagation in underground mines and enabling smart underground mining with an integrated wireless cyber-physical framework;
Underground wireless system may save trapped miners with smart phones, CSU researchers say
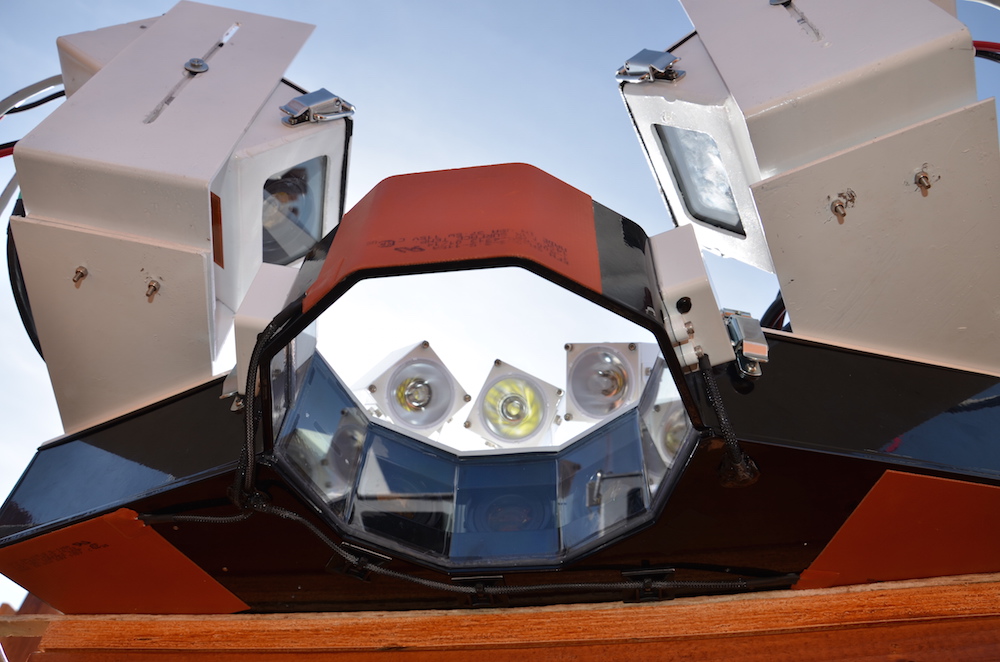
Can you hear me now? CSU research could help miners stay safe - development of the optical/electronic/laser-sensing/image-processing Snowflake Measurement and Analysis System (SMAS);
- RF/microwave applicator system development for biomedical applications;
- development of antennas for biomedical applications;
- revolutionizing engineering departments (RED) – revolutionary redesign of engineering education.
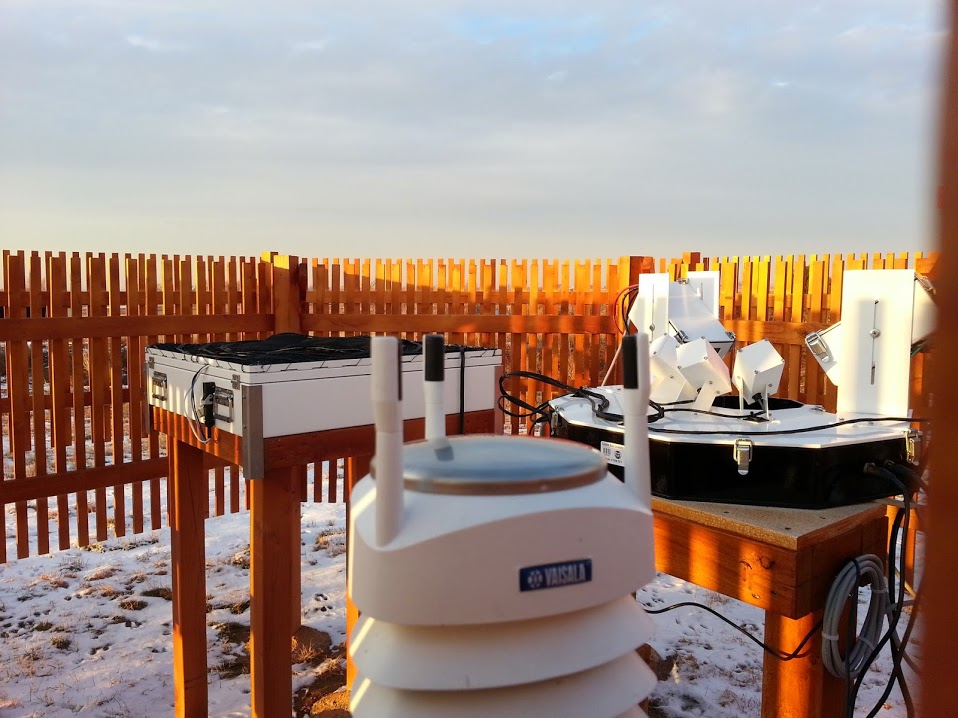
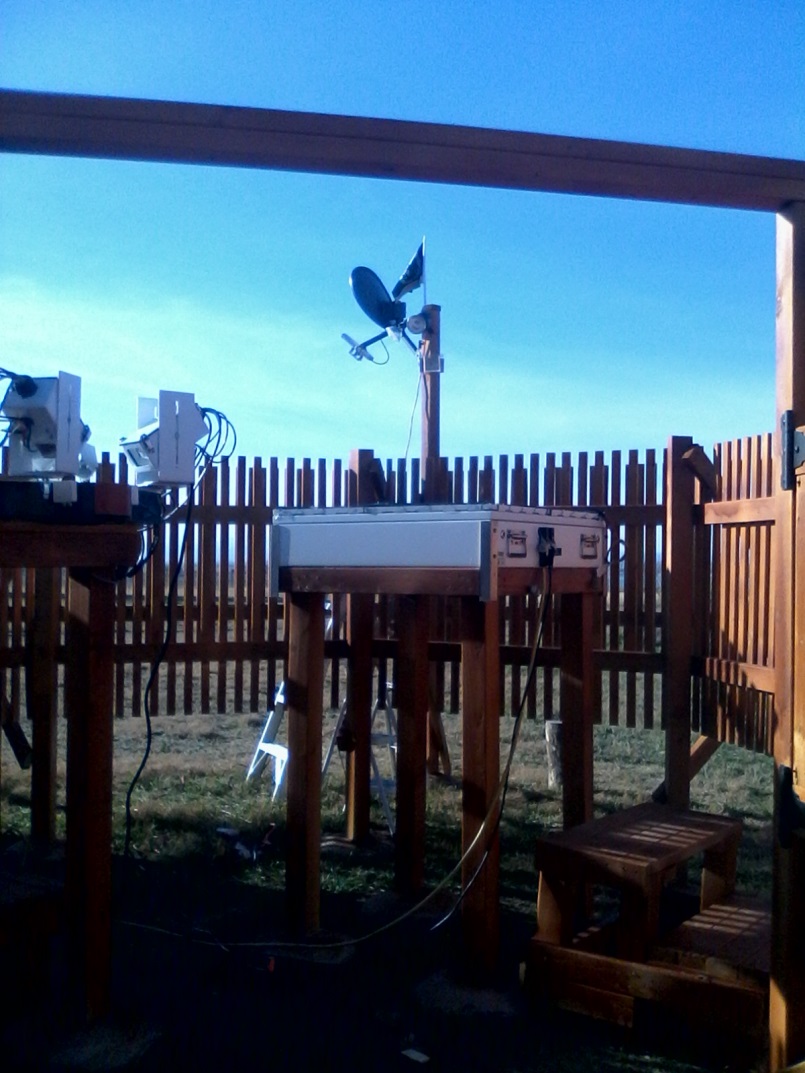
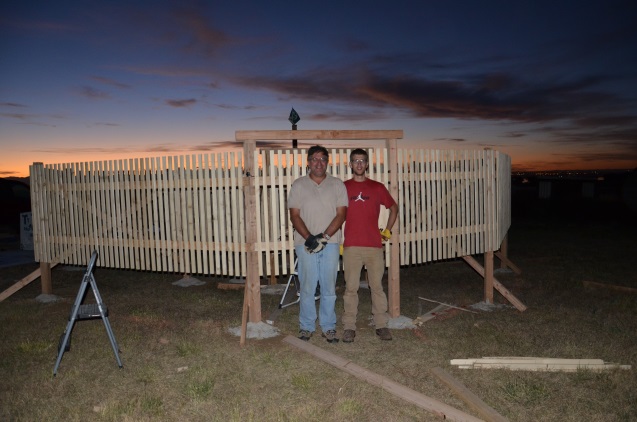
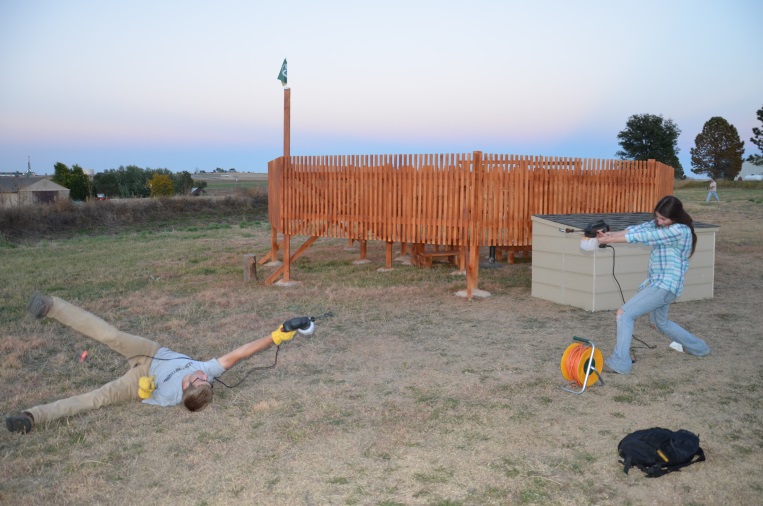
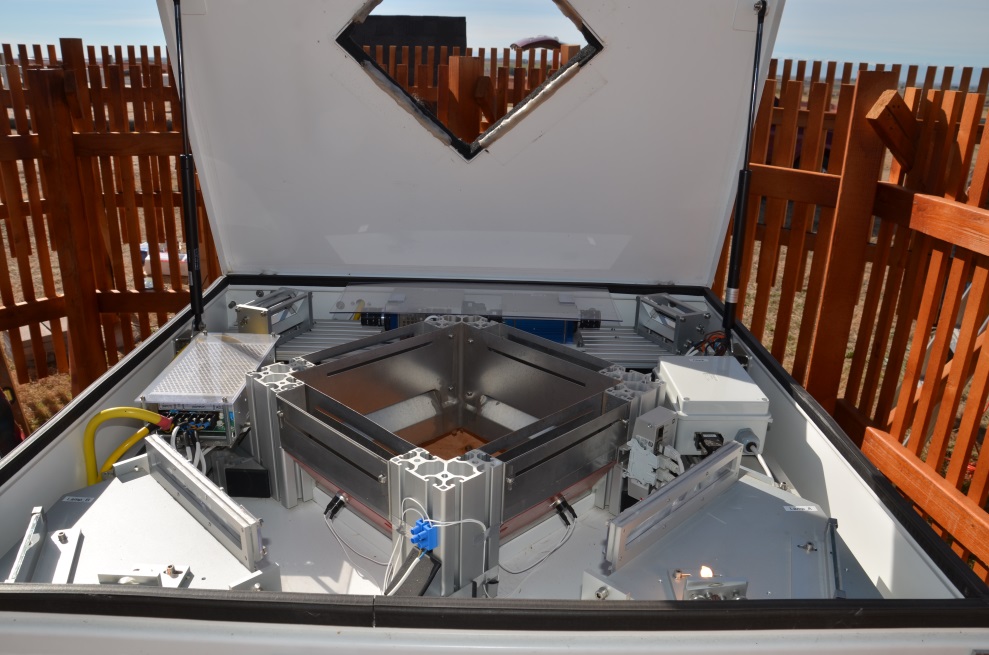
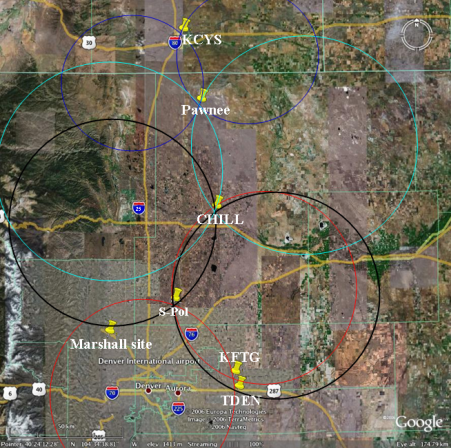
- MASCRAD (MASC + Radar) Snow Observation/Analysis Field Site;
Accurate Characterization of Winter Precipitation Using Multi-Angle Snowflake Camera, Visual Hull, Advanced Scattering Methods and Polarimetric Radar
Measurement and Characterization of Winter Precipitation at MASCRAD Snow Field Site
Snow Precipitation Measurement and Analysis During MASCRAD Winter Observations
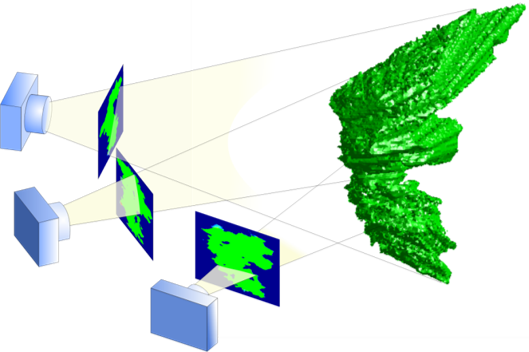
Visual Hull Method for Realistic 3D Particle Shape Reconstruction Based on High-Resolution Photographs of Snowflakes in Freefall from Multiple Views
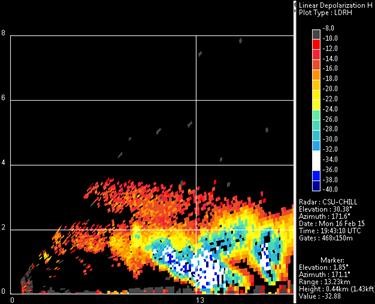
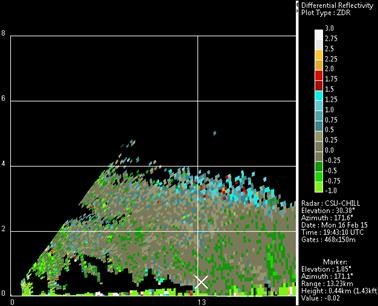
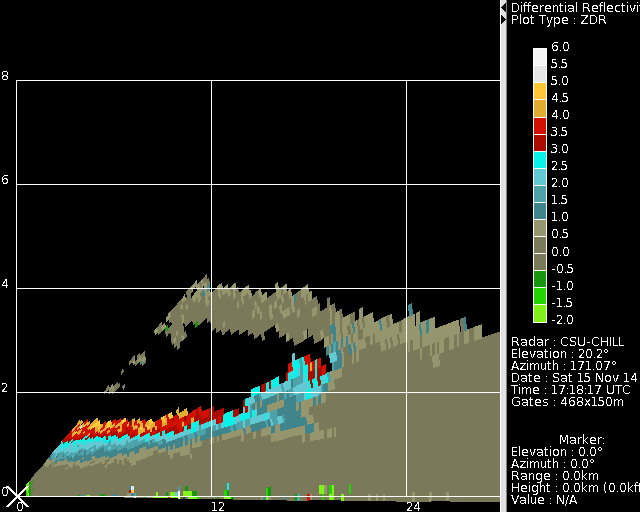
Dual-polarized radar and surface observations of a winter graupel shower with negative Zdr column
DPWX/Initial Multiple Angle Snow Camera-Radar experiment (MASCRAD) project operations: 15 November 2014
Efficient and Accurate Computational Electromagnetics Approach to Precipitation Particle Scattering Analysis Based on Higher-Order Method of Moments Integral Equation Modeling
Let It Snow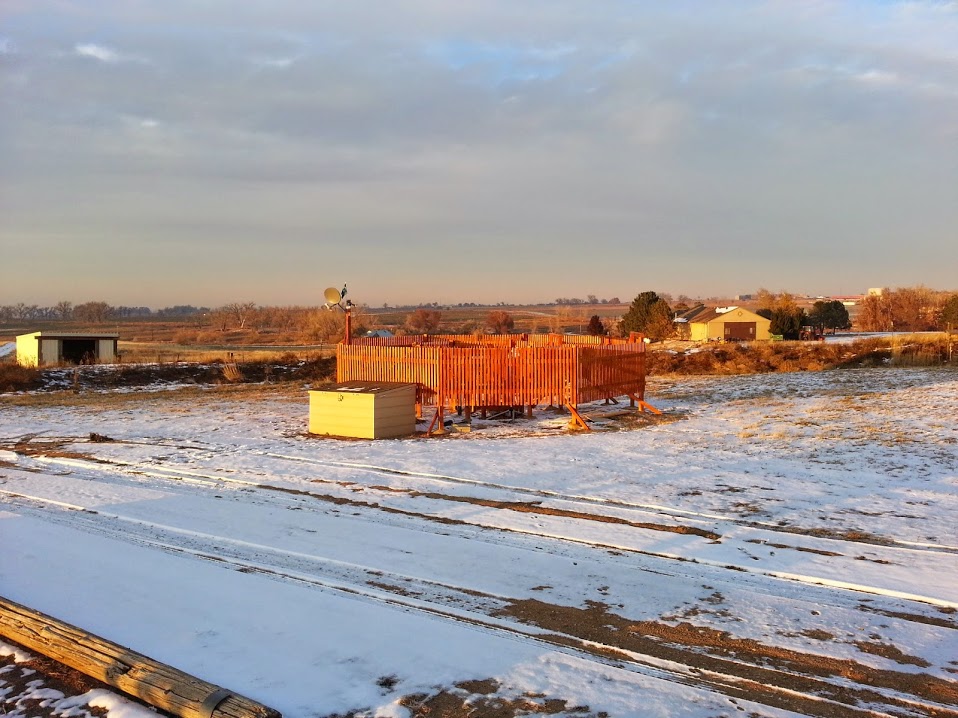





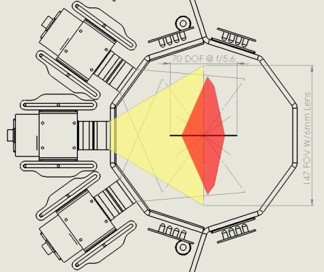
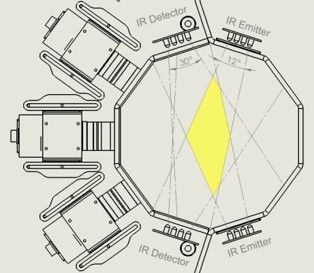















- International Collaborative Experiments for Pyeongchang 2018 Olympic & Paralympic Winter Games, Republic of Korea, ICE-POP 2018;
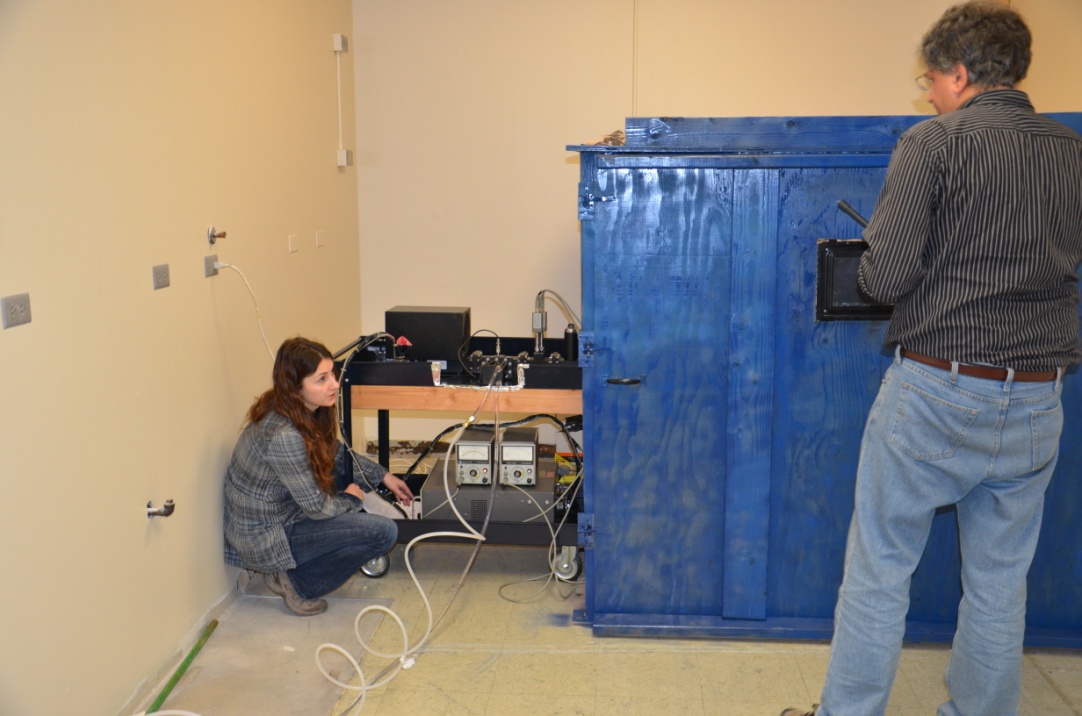





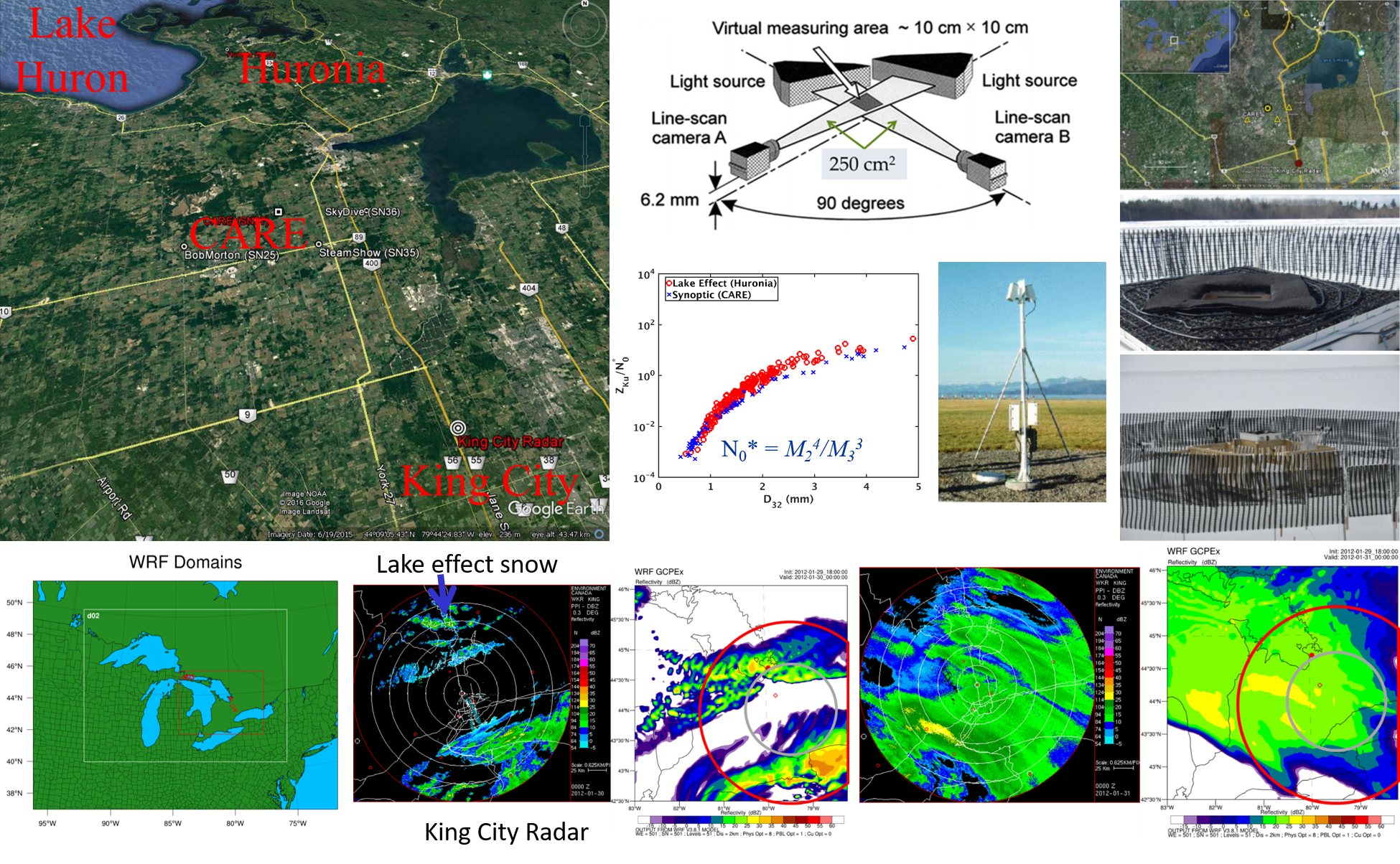


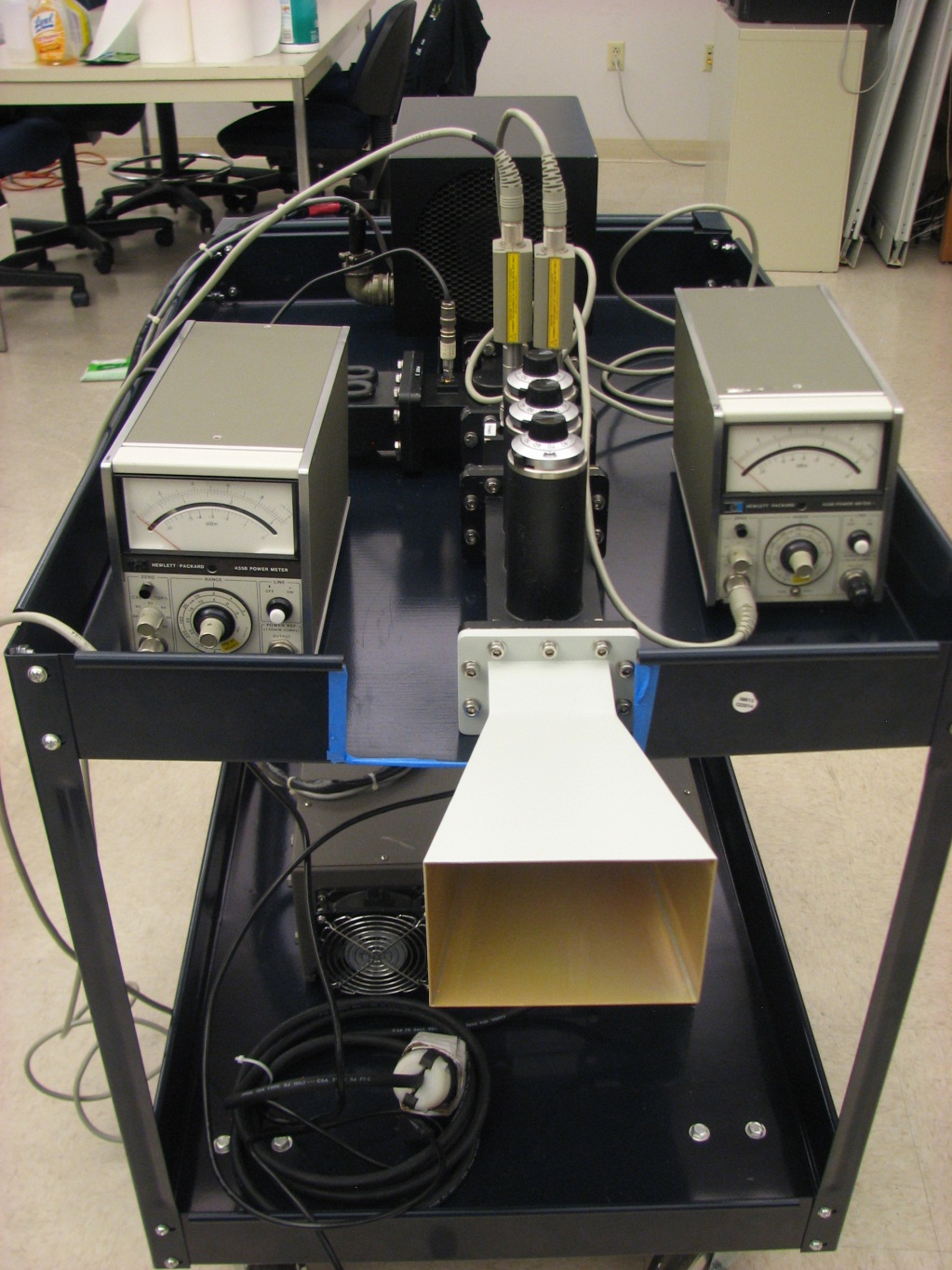












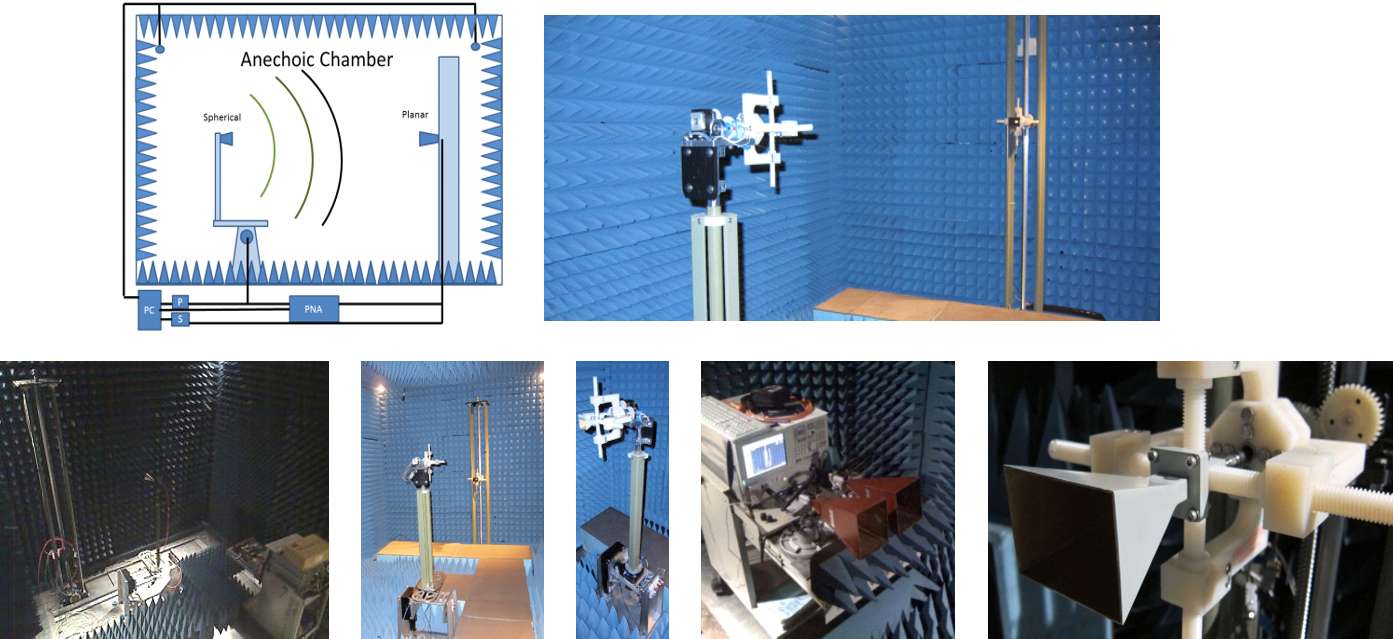
Laboratory and equipment:
Electromagnetics Laboratory, CSU Engineering Building B110, includes a completely computerized and motorized six-axis 10 MHz–50 GHz antenna and scattering test system (three-axis spherical positioning system and three-axis planar positioning system), completely built by students, in a fully anechoic and shielded chamber and a vector network analyzer system (PNA), with time-domain option, oscilloscope, power generators, pulse generator, and other RF equipment.
Antenna test system development: click here
Ph.D. Students
- Milan Ilic (“Higher Order Hexahedral Finite Elements for Electromagnetic Modeling,” 2003)
- Miroslav Djordjevic (“Numerical Methods for Electromagnetic Modeling of Vehicles over a Wide Range of Frequencies,” 2004)
- Eve Klopf (“Optimal Higher Order Modeling Methodology Based on Method of Moments and Finite Element Method for Electromagnetics,” 2011)
- Elene Chobanyan (“Higher Order Volume/Surface Integral Equation Modeling of Antennas and Scatterers Using Diakoptics and Method Of Moments,” 2014).
- Nada Sekeljic (“Transient Analysis of Closed- and Open-Region Electromagnetic Problems Using Higher Order Finite Element Method and Method of Moments in the Time Domain,” 2015)
- Ana Manic (“Fast and Accurate Double-Higher-Order Method of Moments Accelerated by Diakoptic Domain Decomposition and Memory Efficient Parallelization for High Performance Computing Systems,” 2015)
- Sanja Manic (“Electromagnetic Model Subdivision and Iterative Solvers for Surface and Volume Double Higher Order Numerical Methods and Applications,” 2019).
- Cam Key (“Improvements in Computational Electromagnetics Solver Efficiency: Theoretical and Data-Driven Approaches to Accelerate Full-Wave and Ray-Based Methods,” 2020).
- Pranav Athalye (“Designing Novel Radio-Frequency Coils for High Field and Ultra-High Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging,” 2021).
- Jake Harmon (“Accelerated Adaptive Numerical Methods for Computational Electromagnetics: Enhancing Goal-Oriented Approaches to Error Estimation, Refinement, and Uncertainty Quantification,” 2022).
- Stephen Kasdorf (“Full-Wave and Asymptotic Computational Electromagnetics Methods: On Their Use and Implementation in Received Signal Strength, Radar-Cross-Section, and Uncertainty Quantification Predictions,” 2024).
- Hein Thant
- Christopher Erickson
- Ross Stauder
- Nickolas Rhodes












M.S. Students
- Andjelija Ilic
- Ergun Simsek
- Nilanjana De
- Enow Tanjong
- Erdem Yilmaz
- Carlos Flores
- Mubashir Hussain (with Prof. Dayalan Kasilingam)
- Roochi Chopra (with Prof. Steven Nardone)
- Cameron Kleinkort
- Aaron Smull
- Nabeel Moin
- Ryan McCullough
- Marcus Benzel
- Adam Hicks
- Blake Troksa
- Jeremiah Corrado




Undergraduate REU Students
- Christopher Yafrate
- Eric Leveille
- James Davidson
- Ernest Northardt
- She-ming Allen Chen
- Steven Turner
- Amy Standley
- Joseph Kelly
- Eric Smith
- Michael Rader
- Cameron Kleinkort
- Laura Imbler
- Aaron Smull
- Nabeel Moin
- Yoshi Okayasu
- Jacob Hartman
- Chad Paulson
- Mehmed Erkocevic
- Cameron Key
- Jake Harmon
- Jeremiah Corrado
- Corban Yeakley
- Christopher Erickson
- Cody Hundhausen
- Junjiang Lin
- Ce Guo
- Andres Solorzano Solis
- Bryan Johnson
- Aaron Tai
- Peter Walsh
- Luke Aldana
- Corban Yeakley
- Ryan Zonnefeld
- Isaac Jacobson





Postdocs and Senior Research Scientists at CSU
- Dr. Milan Ilic
- Dr. Miroslav Djordjevic
- Dr. Gwo-Jong Huang, Research Scientist/Scholar II
- Dr. Merhala Thurai, Research Scientist/Scholar III
- Visiting Scholar Sponsored at CSU: Dr. José M. Gil, Visiting Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering, CSU, Fall 2009 (on leave from Polytechnic Univ. of Madrid, Spain)


ATMC Telecommunications Lab, UMD
Telecommunications Laboratory, a part of the Advanced Technology and Manufacturing Center (ATMC) at UMass Dartmouth, is a state-of-the-art RF, antenna, and wireless facility providing excellent opportunities for student training and partnering with industry. Its equipment includes:
- 20’ x 12’ x 12’ fully anechoic and completely shielded chamber (Cuming Microwave Corporation)
- 7-axis hybrid planar/spherical/cylindrical completely computerized near-field antenna test system, with 6’ x 6’ x 6’ scanning area and far-field extension (Antcom Corporation)
- 8510E vector network analyzer system (Agilent Technologies)
Participation on Grants and Contracts at University of Colorado and University of Belgrade
- Vivaldi antenna arrays for square kilometer array (SKA) radio telescope, with Prof. Zoya Popovic, Antenna/Microwave Lab, ECE Dept., University of Colorado, Boulder.
- Reflector antenna modeled after an external ear of a bat species Plecotus auritus and its dual-frequency biosonar, with Prof. Zoya Popovic, University of Colorado, Boulder.
- Optical control of microwave arrays: photonically tuned slot antennas, with Prof. Zoya Popovic, University of Colorado, Boulder.
- Optical antenna and array design (consulting project), with Prof. Zoya Popovic, Boulder Colorado.
- Design and realization of directive antenna arrays with electrically small unconventional reflectors, with Prof. Branko Popovic, Prof. Zoya Popovic, and Prof. Edward Kuester, University of Belgrade, Yugoslavia and University of Colorado, Boulder.
- Development of one-port, multiply excited (OPOMEX) antennas (generalized COCO antennas), with Prof. Branko Popovic and Prof. Zoya Popovic, University of Belgrade, Yugoslavia and University of Colorado, Boulder.
- Design of supergain antenna arrays, with Prof. Branko Popovic and Prof. Zoya Popovic, University of Belgrade, Yugoslavia and University of Colorado, Boulder.
- Development of efficient and accurate electromagnetic simulation techniques for wire, plate, and dielectric antennas and scatterers, with Prof. Branko Popovic, School of EE, University of Belgrade, Yugoslavia.
- Design of large optimal NEMP-simulator antennas, with Prof. Branko Popovic, University of Belgrade, Yugoslavia.
- Design and realization of new classes of loaded broadband wire antennas, with Prof. Branko Popovic, University of Belgrade, Yugoslavia.
- Design and realization of log-periodic wire VHF/UHF TV antennas, with Prof. Branko Popovic, University of Belgrade, Yugoslavia.
- Design and realization of a class of GPS antennas and communication antennas situated inside automobiles – for theft protection and tracking system (consulting project), with Prof. Branko Popovic, Belgrade, Yugoslavia.
- Design and experimental testing of shielded rooms in health centers, with Prof. Branko Popovic, University of Belgrade, Yugoslavia.


Electromagnetics and Engineering Education Research

- New Textbook “Electromagnetics” with PEARSON Prentice Hall. B. Notaros is the author or coauthor of several textbooks in electromagnetics and in fundamentals of electrical engineering (basic circuits and fields). In addition, he has just published his new comprehensive textbook “Electromagnetics” (840 pages) for undergraduates with PEARSON Prentice Hall. The new book introduces many unique pedagogical features not present in any of the many existing undergraduate electromagnetics textbooks [there are an extremely large number (~30) of quite different textbooks for undergraduate electromagnetics available and “active” – perhaps more than for any other discipline in science and engineering]. In specific, it provides several nonstandard theoretically and practically important chapters and sections, new style and approaches to presenting challenging topics and abstract EM phenomena, numerous modern supplements, original teaching and learning tools, and some unique recipes and pedagogical guides for electromagnetic field computation and problem solving. It is meant as an “ultimate resource” for undergraduate electromagnetics.
- New Textbook “MATLAB®-Based Electromagnetics” with PEARSON Prentice Hall (416 pages), published in May 2013. This is a self-contained textbook that can be used either as a supplement to any available electromagnetics text or as an independent resource. Essentially, the book unifies two themes: electromagnetics using MATLAB and MATLAB for electromagnetics; namely, it presents and explains electromagnetics using MATLAB on one side and develops and discusses MATLAB for electromagnetics on the other. As opposed to other available electromagnetics texts that feature some use of MATLAB, the new book effectively “implements” literally all topics and concepts in undergraduate electromagnetic fields and waves, from the ones in electrostatics to those in antennas, in MATLAB. This is by far the most complete and ambitious attempt to use MATLAB in undergraduate (and overall) electromagnetics education.
- New Textbook “Conceptual Electromagnetics” with CRC Press, Taylor and Francis, LLC (530 pages), in production/press (2017). This is a standalone textbook on Conceptual Electromagnetics that presents and explains the entire EM solely using conceptual questions interwoven with the theoretical narrative and basic equations. It combines fundamental theory and a unique and comprehensive collection of as many as 888 conceptual questions and problems in EM. Conceptual questions and problems of this scope and intent are completely new in EM area, and in practically all ECE areas. Also, this is one of the most complete and ambitious attempts to use them in science and engineering education overall. This book resonates very well with modern learner-centered pedagogies and practices that have recently gained a lot of attention by educators in science and engineering, and are paving their way as a preferred mode, or a major component, of class delivery and instruction.
- Conceptual Questions in Electromagnetics, 160 pages, an e-supplement to the new textbook “Electromagnetics” published by PEARSON Prentice Hall. This collection provides 500 Conceptual Questions – these are multiple-choice questions that focus on the core concepts of the material, requiring conceptual reasoning and understanding rather than calculations. Pedagogically, they are an invaluable resource. They can be given for homework and on exams, and are also ideal for interactive in-class questions, explorations, and discussions (usually referred to as active teaching and learning), for student-to-student interaction and students teaching one another (so-called peer instruction, initiated by Eric Mazur in introductory physics), and for team work and exchange of ideas (collaborative teaching/learning). In addition, conceptual questions are perfectly suited for class assessments, as partial and final assessment instruments for individual topics at different points in the course and for the entire class.
- Computer Exercises in Electromagnetics Using MATLAB, 350 pages, an e-book (separate ISBN), supplement to the new textbook “Electromagnetics” published by PEARSON Prentice Hall. There are a total of 478 MATLAB exercises, to supplement problems and conceptual questions. The Exercises include 135 tutorials with detailed completely worked out solutions merged with listings of MATLAB codes (m files), 58 movies developed and played in MATLAB, 156 figures generated in MATLAB, 16 graphical user interfaces (GUIs) built in MATLAB, etc. Assignments of computer exercises in parallel with traditional problems can help students develop a stronger intuition and a deeper understanding of electromagnetics and find it more attractive and likable. Moreover, this approach, requiring MATLAB programming, actively challenges and involves the student, providing additional benefit as compared to a passive computer demonstration.
- Electromagnetics Concept Inventory (EMCI), an assessment tool for measuring students’ understanding of fundamental concepts in electromagnetics. This work was supported by the Engineering Education Program of the National Science Foundation, through the NSF Foundation Coalition grant. The EMCI is especially important in light of the new accreditation standards in engineering – ABET 2000 Criteria (the key word in these criteria is ‘assessment’). (A copy of the EMCI can be obtained upon request, with proper identification, at notaros@colostate.edu).
- Assessment Methodologies for Engineering Education – participated in several national meetings and multi-university research studies devoted to conceptual assessment instruments and other assessment techniques, as well as curricular reforms, in engineering education. Participated in organization and delivery of panel sessions on the tools for assessing conceptual understanding in engineering sciences at the ASEE/IEEE Frontiers in Education Conferences and the Concept Inventory Developers Meetings, gave talks and has papers on concept inventory assessment instruments for electromagnetics education.
- Also, participated (by invitation) in 2014 Reinvention Center National Conference, November 14-15, 2014, Arlington, Virginia. The Reinvention Center’s mission is “Advancing Undergraduate Education in America’s Research Universities.”
- “Creativity Thread Champion” for the NSF Revolutionizing Engineering Departments (RED) Project. B. Notaros is one of the principal contributors to the five-year NSF Revolutionizing Engineering Departments (RED) Project in the ECE Department at CSU (PI: Anthony Maciejewski, ECE Dept. Head). As one of the only six engineering and computer science departments in the first cohort of NSF RED awardees, we are implementing changes that reimagine the roles of the faculty, moving away from teaching courses in isolation to an integrated, collaborative structure. Key faculty leaders are assigned as “Thread Champions” to interweave Foundations, Creativity, and Professional Formation threads throughout the program, while working with fellow faculty to continue fostering deep knowledge of the discipline and with “Integration Specialists” to synthesize content and illustrate how fundamental concepts are interrelated. These efforts span the entire undergraduate experience, with special attention to the critical technical core of the junior year. Prof. Notaros is the “Creativity Thread Champion” for the RED Project. He also is a leader in developing and implementing electromagnetics learning studio modules (LSMs) and in knowledge integration (KI) of EM LSM concepts with those from signals/systems and electronics, as an essential part of the RED revolution in the ECE Department. After the scalability has been investigated and enhanced, we anticipate that this project and its outcomes will potentially have a transformative impact on the ECE and engineering education globally.

