1. Software Techniques
2. Programming the DS1075 Programmable Clock
3. External Clocking
1. Software Techniques
In this section, three techniques are illustrated to effectively "slow down" the clock for the DS1075 programmable clock. All techniques are for the same program implementation, with increasing complexity. The program being illustrated here is a 4-bit binary up counter where the results are displayed on a 7-segment display. The first technique is a simplier design and employs a method where extra bits are used for counting the 50MHz clock counts and then only using the 4 Most Significant Bits (MSBs) for display on the 7-segment display. The second technique is a better design in that it implements a counter to count the clock cycles coming into the FPGA. Once the counter has achieved a pre-determined delay, this counter "clocks" the 4-bit binary up counter. The results are displayed on a 7-segment display. The third technique is a variation of technique 2 (or vice versa).

2. Programming the DS1075 Programmable Clock
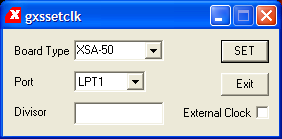
The XESS GSXSETCLK is the utility program which programs the programmable clock. A divisor in the range from 1 to 2052 will permit the programmable clock to divide down the 100MHz clock by the divisor. In other words, the programmable clock has a range of 100MHz down to approximately 48.7KHz. Simply enter the desired divisor and press "SET". Even though the DS1075 programmable clock is rated to accomodate 100MHz, The XESS XSA-50 protoboard has set the default (clocking) divisor to be 2. In other words, the FPGA is clocked at 50MHz. Consequently, if a user is using the programmable features of the DS1075 programmable clock via the GXSSETCLK utility, to restore the XSA-50 protoboard to it's default clocking configuration, one must restore the default divisor using the GXSSETCLK utility to 2. This will store 2 as the divisor in the DS1075 programmable clock's EEPROM. Follow the instructions that will "pop-up" when using this feature.